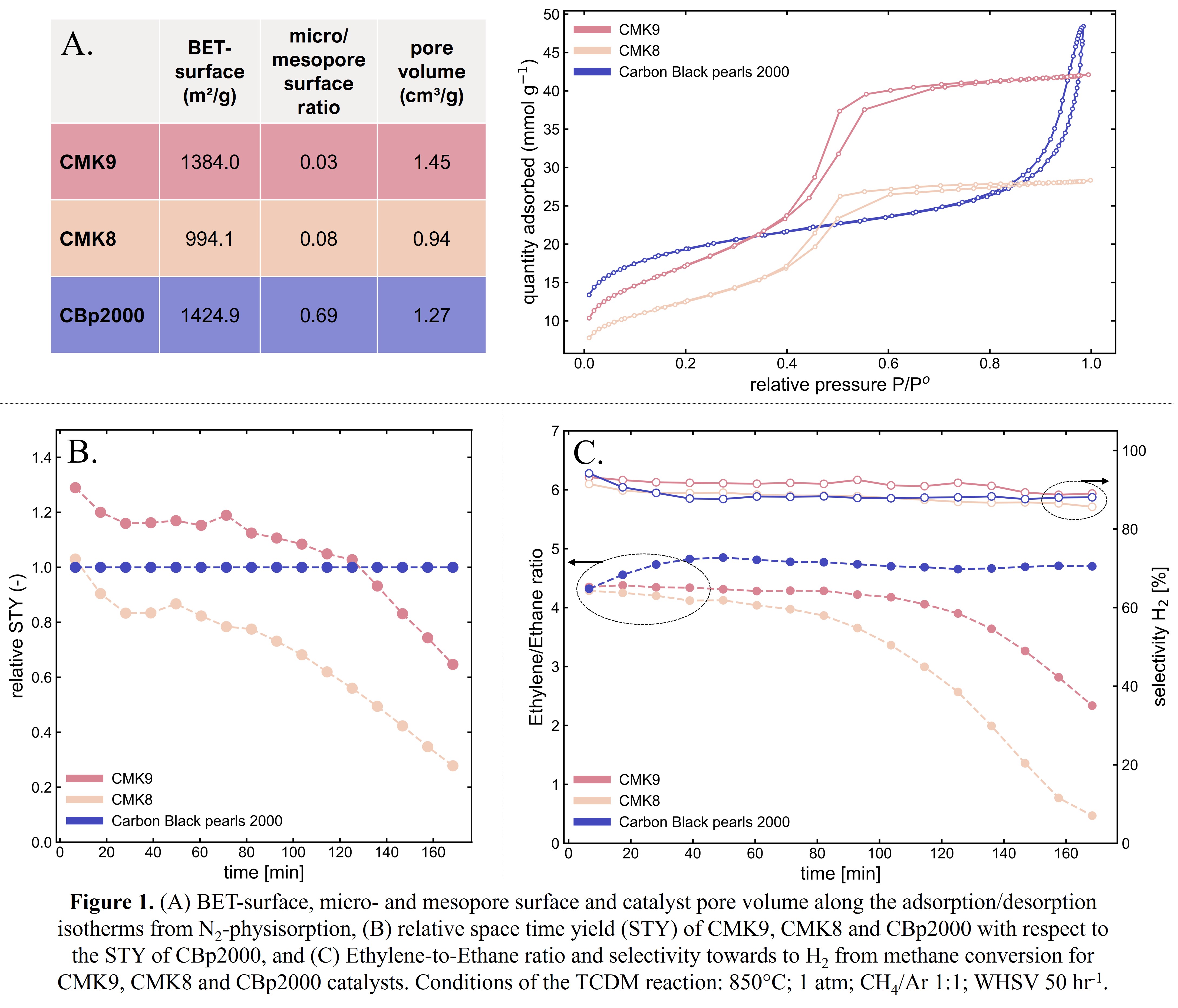
The thermocatalytic decomposition of methane (TCDM) presents a promising approach for sustainable hydrogen (H
2) production alongside solid carbon from methane, circumventing CO
2 emissions. However, a major challenge persists in the form of fast catalyst deactivation due to the substantial accumulation of carbon deposits on the catalyst surface during methane pyrolysis. Ordered mesoporous carbons (OMC’s) with designated pore structures combine a high specific surface area and pore volume, which enables them to accumulate large amounts of carbon deposits, thus resulting in a highly stable catalyst. Therefore, two innovative OMC’s, denoted as CMK8 and CMK9, have been synthesized via the hard-templating technique, characterized through N
2-physisorption, Raman spectroscopy and XPS, and tested alongside carbon black pearls 2000 (CBp2000) in a fixed bed reactor at 850°C and atmospheric pressure for the TCDM process. The materials demonstrate a negative structure of silica KIT-6’s mesoporous template, which was totally filled with the poly(furfuryl alcohol) carbon precursor for CMK8. Partial filling was carried out for CMK9, resulting in a higher BET-surface area and higher pore volume compared to CMK8. Next, Raman spectroscopy showed that cokes deposition upon methane pyrolysis results in a decrease of the graphitic order of the carbon materials. Based on performed activity tests, it is demonstrated that CMK9 exhibits a 30% superior initial space-time yield (STY) and higher selectivity towards H
2 (92%) compared to CBp2000. In contrast, CMK8 initially demonstrates a comparable STY to CBp2000, which is followed by a rapid decline. Therefore, introducing a surplus of catalyst surface area and pore volume by partially filling the KIT-6 template yields an improved activity and stability. These findings agree with XPS measurements, indicating that CMK9 possesses the highest number of defects among the tested materials based on the full width at half maximum of the C1s-peak, thus yielding the highest initial STY.