Rising demand for hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2) has attracted attention towards more sustainable production technologies. Photocatalysis is an alternate eco-friendly approach for synthesizing H
2O
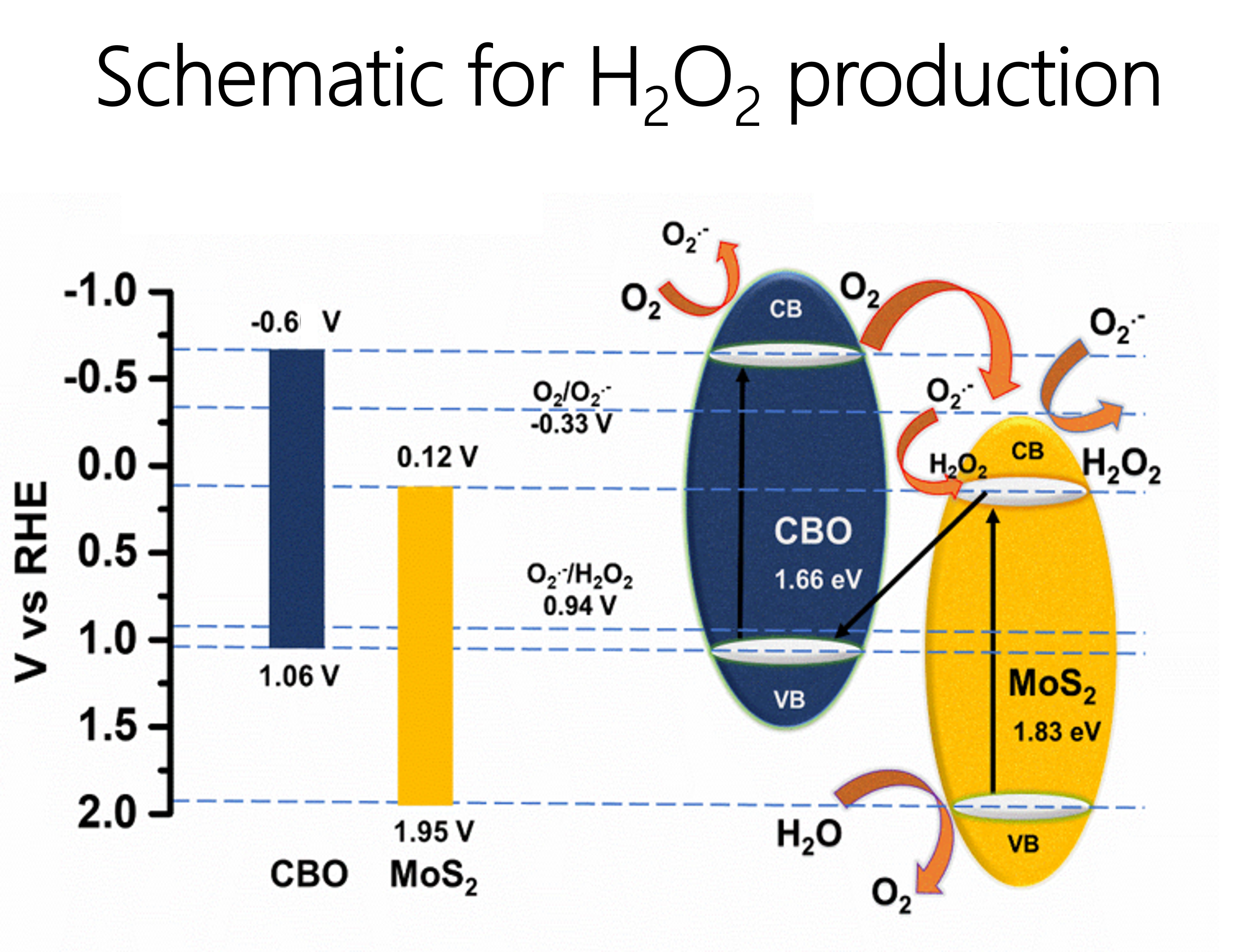
2, without any byproducts as well as offering advantages such as low cost, and no release of toxic chemicals. Two-dimensional (2D) layered transition metal chalcogenide (TMC) photocatalysts are good at light harvesting due to their high specific surface area and exhibit excellent optoelectronic properties which makes them suitable for environmental remediation and energy production. Metal sulfides have a narrower band gap, which improves their light absorption ability in the visible spectrum. However, they often suffer from low quantum yield and high charge recombination rate. This issue can potentially be addressed through suitable band edge line-up of two or more semiconductors, particularly z-scheme systems, which have superior charge separation and light harvesting properties. The present study explores a z-scheme system with CBO (Copper bismuth oxide) and MoS
2 (molybdenum sulfide), which have good light harvesting abilities and efficient charge separation. CBO has a narrow bandgap, good light harvesting capability, and high negative conduction band potential. And MoS
2 is recognized as an excellent co-catalyst for advanced oxidative processes with improved light harvesting, efficient interface charge transfer, and separation. The synthesized catalyst, CBO@ MoS
2, has been characterized using several techniques, including XRD, Raman, PL, UV-Vis, and TEM. The catalyst has shown a significantly higher H
2O
2 production rate of 1457 µM h
-1 which is an order of magnitude higher than the pure components. The improved photocatalytic activity of CBO@MoS
2 is mainly attributed to the efficient separation of the electron-hole pairs due to staggered band alignment and the z-scheme heterojunction that retains the strong redox ability of both CBO and MoS
2. Mechanistic insight is also provided using radical trapping and several other experiments.