2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(625f) Sn-Beta Active Site Quantification Via Catalytic Site Titrations – Impact of Titrant and Solvent Molecules
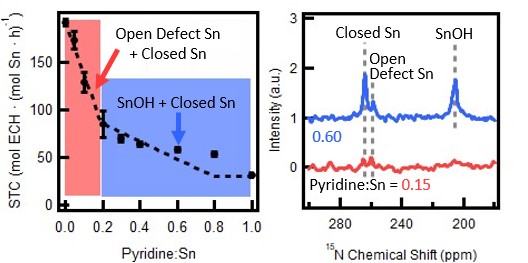
The effects of titrant (triethylamine, pyridine, 2,6-lutidine) and solvent (hexane, dichloromethane) on titration experiment results are investigated using Sn-Beta for epoxide ring opening (ERO) reactions. Pyridine/hexane is identified as a good titrant/solvent combination that distinguishes high-, low-, and no-activity regimes in the titration experiment data. 15N-labeled pyridine/hexane is used to connect titration experiments with 15N NMR. 15N NMR results suggest that pyridine titrates sites as follows: (1) In the high-activity regime, both open-defect and closed Sn sites, then (2) in the low-activity regime, additional closed Sn sites as well as SnOH groups. Based on these results, open-defect sites are identified as the singular high-activity site. Ongoing work will resolve the role of SnOH groups and hydrolyzed-open Sn sites in ERO. Overall, this work highlights titration experiments as an insightful site quantification technique when combined with NMR. Furthermore, the results will help to establish valuable synthesis-structure-activity relationships for Sn-Beta materials.