2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(604f) Tailoring Polyethene Properties: An Investigation into Zirconocene Catalyst Activity and Reaction Parameters
Authors
Priyanka Ghar, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
Soumita Basu Mallick, IIT Kharagpur
Narayan Pradhan, IIT Kharagpur
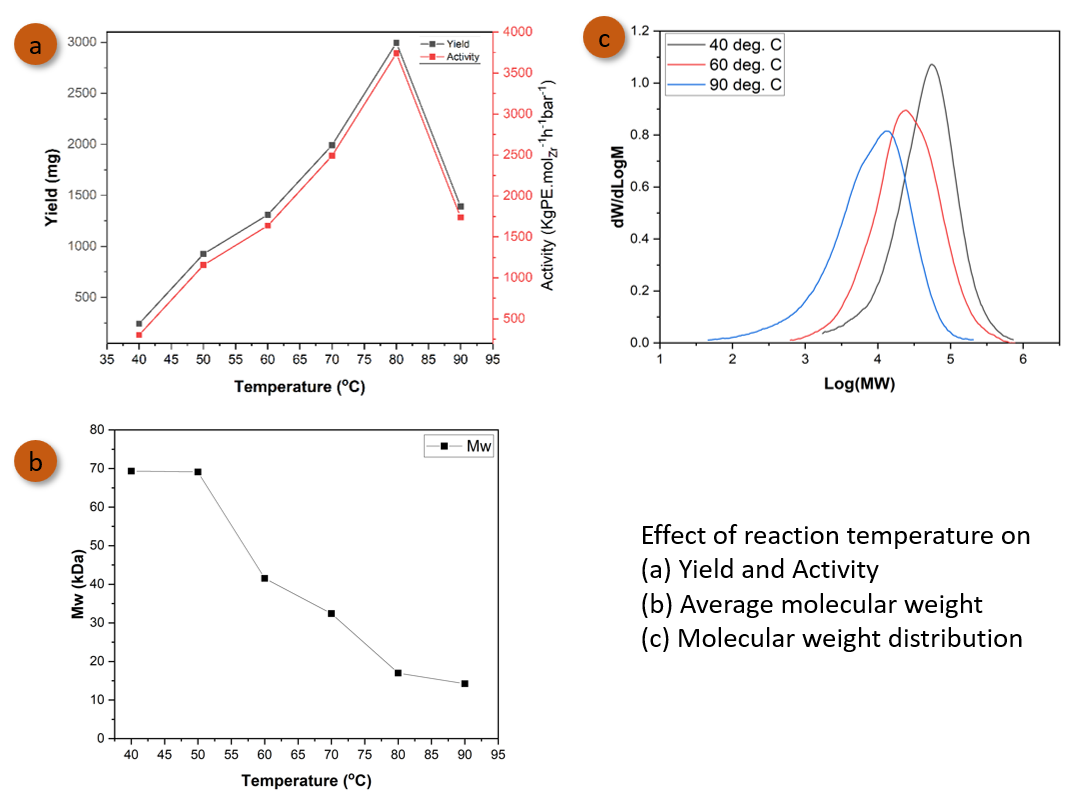
Under global demand for polyethene across various industries, homogeneous metallocene catalysts have emerged as a preferred choice over traditional heterogeneous Ziegler-Natta catalyst. Earlier, activation of metallocene catalyst using methyl aluminoxane (MAO) has shown promising results, however requirement of a large amount of MAO for activation made the olefin polymerization process expensive. On the other hand, activation using Organoborate compounds in conjunction with alkylaluminium has demonstrated the superiority of the production of polyethene with tailored properties. While, polyethene properties also relate to different reaction parameters such as reaction temperature, time, catalyst concentration and cocatalyst ratio. However, significant constructive research activities on the correlation between properties and reaction parameters are hardly explored in the literature. This work, therefore, investigates how these reaction parameters can significantly influence the catalyst activity, MW and MWD of synthesized polyethene. To achieve this, commercial metallocene catalysts such as rac-Ethylenebis(indenyl)zirconium(IV) dichloride were activated by tetrakis(perfluorophenyl)borate where Triisobutylaluminium (TIBA) was used as cocatalyst. Following Schlenk line method, the reactions were conducted in the solution phase, using toluene as a solvent with temperatures ranging from 40 to 90°C, and catalyst concentrations ranging from 0.02x10-3 to 0.08x10-3 mol. L-1, and reaction times varied up to 30 minutes. The effect of [Al]/[Zr] ratio was also investigated in the range of 200-400. Synthesized polyethene properties, including molecular weight (MW) and molecular weight distribution (MWD), were determined using high-temperature gel permeation chromatography (GPC). It is observed from the results that the reaction temperatures showed significant impact on catalyst activity, increasing from 302.5 kgPE.molZr-1.h-1 to 3740 kgPE.molZr-1.h-1 where highest activity was obtained at 80oC. In addition, higher molecular weight was achieved at lower temperatures with narrow MWD. On the other hand, the influence of reaction time showed the highest catalyst activity, 15510 kgPE.molZr-1.h-1 at the beginning of the reaction and diminished as the reaction progressed, resulting in the gradual changes in molecular weight after a few minutes of the start of the reaction. Increasing catalyst concentration by 4 folds also led to decrease in MW from 124.3 kDa to 71 kDa, while increasing [Al]/[Zr] ratio resulted in an increase in catalyst activity, but decrease in MW. These results can be useful for optimizing reaction parameters to obtain the desired MW and MWD of polyethene.