2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(5d) Identifying Effects of Phosphorous in Transition Metal Phosphides for Selective Hydrogenolysis of Hindered C–O Bonds
Authors
Hansel Montalvo-Castro, University of Florida
Justin Atlas, University of Florida
Alvaro Loaiza, Louisiana State University
Craig Plaisance, Louisiana State University
David Hibbitts, University of Florida
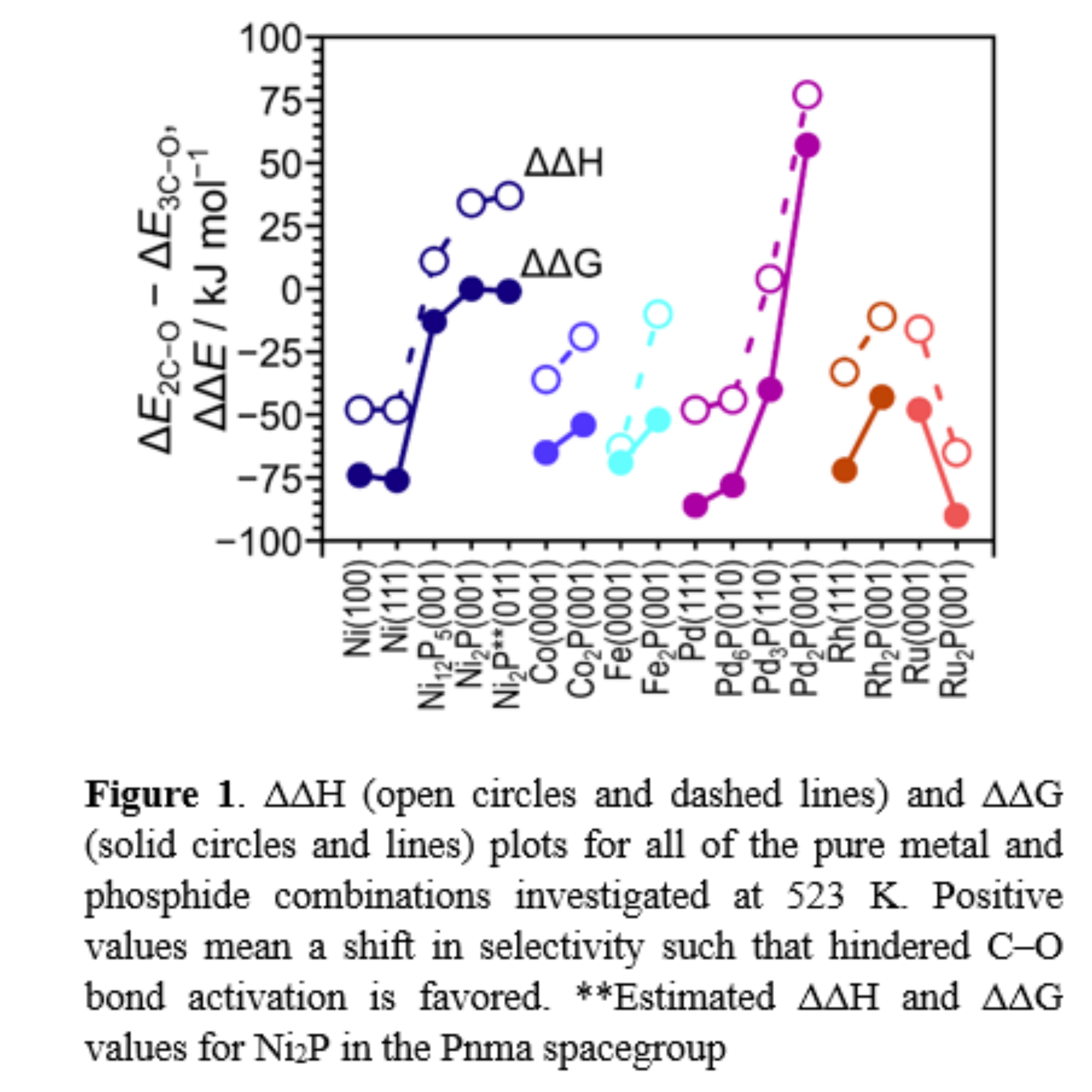
Contrasts between hindered and unhindered C–O activations within biomass derived molecules can be investigated using 2-methyltetrahydrofuran (MTHF) as a model compound. MTHF contains a furan ring whose O atom has neighboring secondary (2C) and tertiary (3C) carbons. Experiments and DFT suggest that adding P to Ni results in a shift in selectivity towards a preference for 3C–O activation over the undesired 2C–O reaction. Activation enthalpy (ΔΔH) and free energy (ΔΔG) differences (ΔG2C–O – ΔG3C–O) were calculated to predict selectivity with the Ni(111) surface having lower ΔΔH and ΔΔG values (−48 and −70 kJ mol−1, respectively) than Ni2P(001) (34 and 0 kJ mol−1), suggesting that selectivity increases with P content [1]. Recent work attempted to understand the reason why P causes this shift in selectivity by investigating electronic effects of P addition through other transition metal phosphides isostructural to Ni2P(001). Pd2P, Rh2P Fe2P, Ru2P and Co2P (in addition to Ni2P) were all investigated and a nearly ubiquitous shift in selectivity was observed with all phosphide materials except Ru2P showing greater ΔΔH and ΔΔG values than their pure metal counterparts (Fig. 1) [2]. In the present contribution, we continue this work by investigating the effects of geometry (crystal structure) on selectivity and P content for a different series of metal phosphides. We contrast Ni2P in the Pnma spacegroup to Ni2P in the original P62m spacegroup, and find that, at least between these two spacegroups, there is an almost negligible shift in selectivity. For Pd, we contrast Pd, Pd6P, Pd3P, and Pd2P, and show a monotonic increase in ΔΔH and ΔΔG values (consistent with greater 3C–O activation selectivity) like that observed for Ni phosphides. Overall, we see that P incorporation increases selectivity towards 3C–O activation for all metals except Ru.
References
[1] ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7141–7157. [2] J. Catal. 2023, 421, 403–418.