2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(5a) Structural Effects on the Selectivity of Electrocatalytic Hydrogenation of Cis,Cis-Muconic Acid over Palladium (Hydride)
Authors
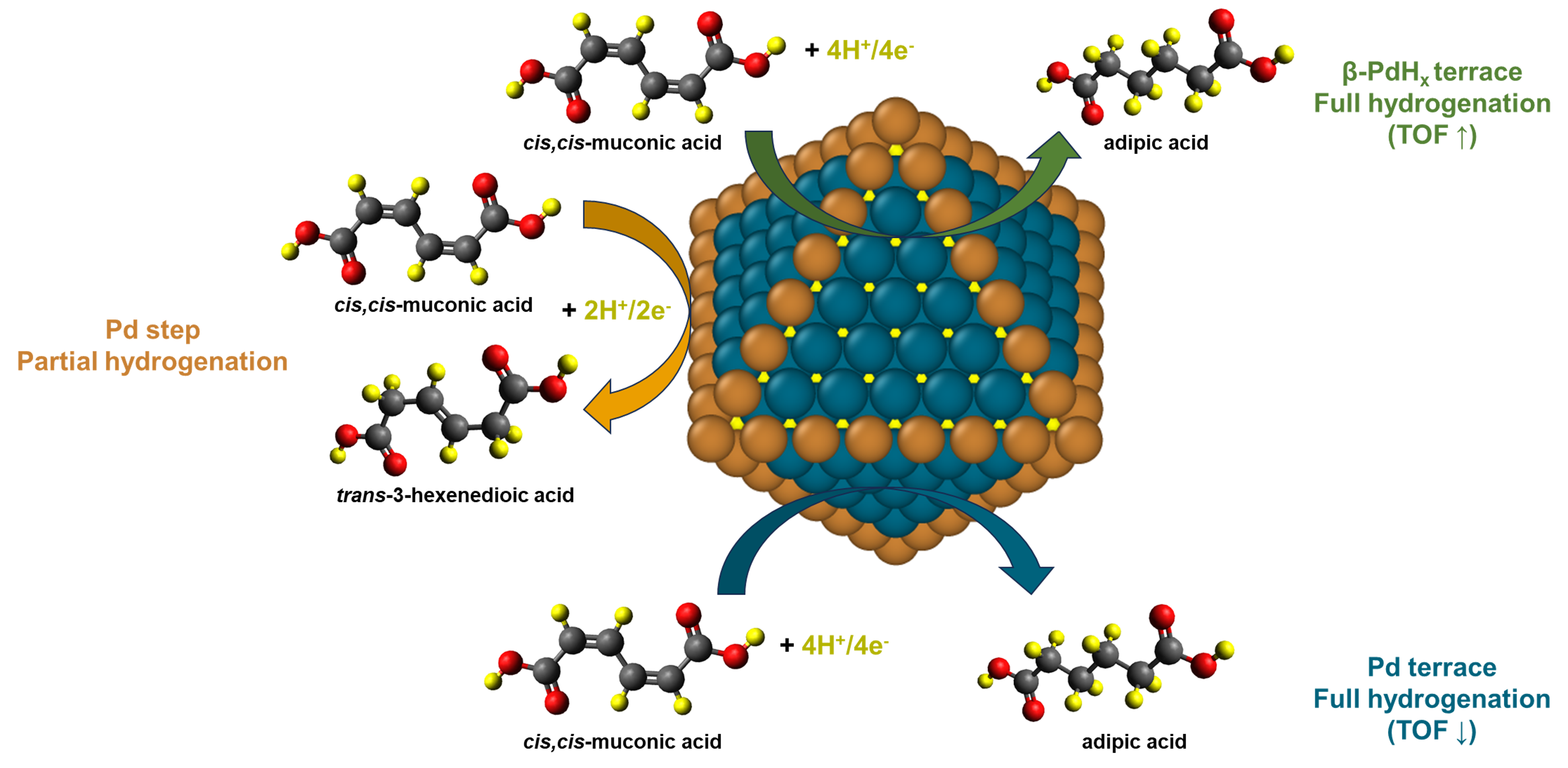
Our experiments on commercial Pd/C showcase remarkable activity of ccMA ECH with high conversion (>90%) and selectivity (>95%) to AA at low pH and -0.40 VAg/AgCl. Cyclic voltammetry suggests the dynamic interplay of protons at the surface and in the subsurface of Pd nanoparticles, indicating the complex effect of the surface microenvironment on the observed reaction kinetics.
We apply density functional theory (DFT) calculations to understand the effect of lattice hydrogen on ccMA ECH selectivity towards t2HDA, t3HDA, and AA, considering models of a bulk β-PdHx phase as well as those with hydrogen simply in the first subsurface layer. We find that the β-PdHx can enhance AA selectivity relative to bare Pd surface due to weak binding strength induced by lattice hydrogen of the β-PdHx phase. Further, we show that this effect is structure sensitive – while the β-PdHx at terrace sites of Pd nanoparticles (NP) enhances AA selectivity, β-PdHx at undercoordinated step sites of Pd NP has no significant effect on reaction kinetics. We calculate that this structure sensitive effect is due to the strong binding of organics and relative instability of subsurface hydrogen at steps. Overall, these results suggest that β-PdHx might be more active than bare Pd for ccMA ECH under acidic conditions.
References:
(1) Patel, D. M. et al. Green Chem. Advance Article (2024).
(2) Dell’Anna, M. N. et al. Green Chem. 23, 6456–6468 (2021).