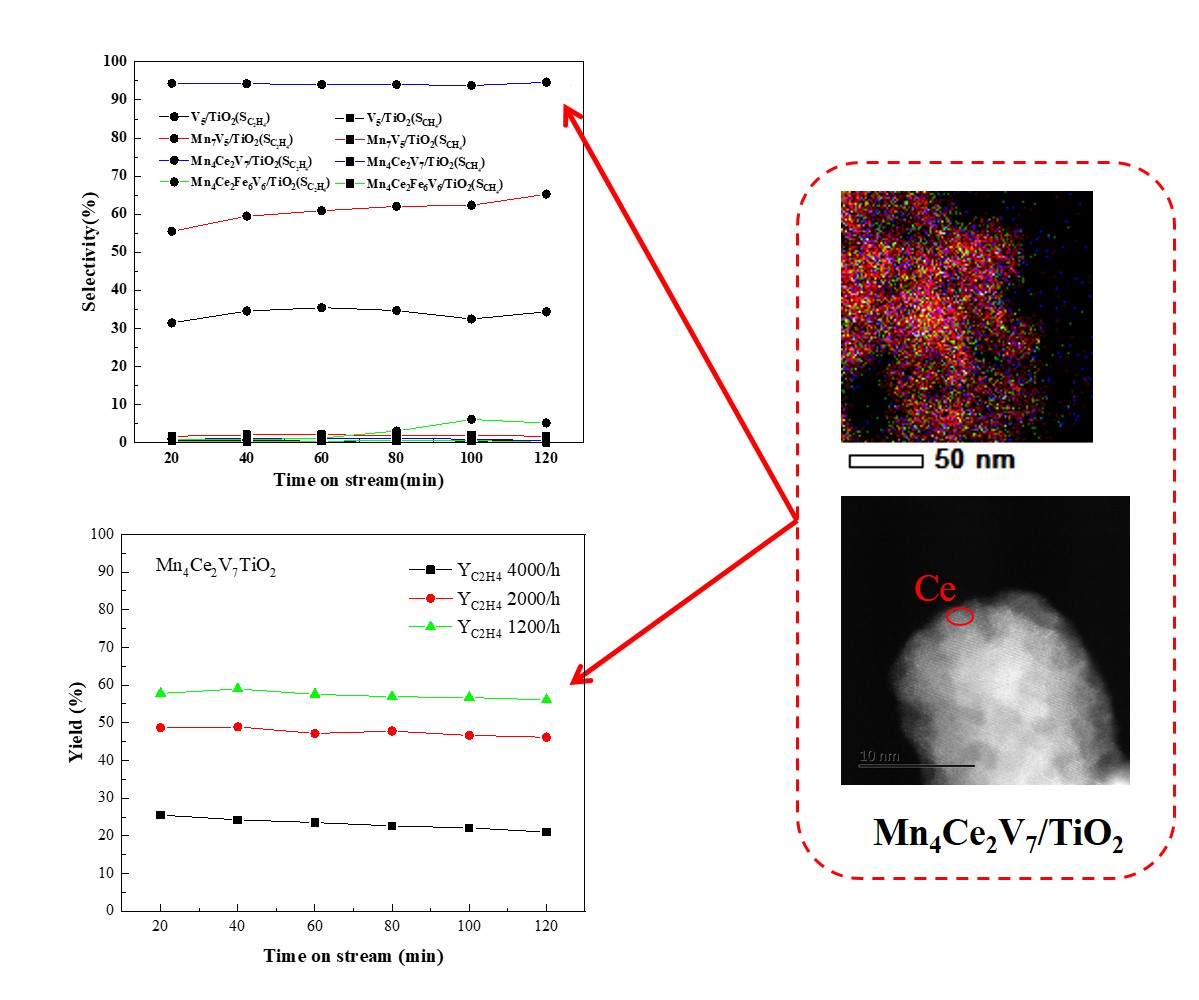
Ethane oxidative dehydrogenation appears to be one of the most promising technologies in terms of potential industrial applications for ethylene production. However, creating a catalyst with improved selectivity without sacrificing catalytic activity remains a difficult issue. In this study, a systematic set of catalysts (V
5TiO
2, Mn
7V
5TiO
2, Mn
2Ce
2V
7TiO
2 and Mn
4Ce
2Fe
6V
6TiO
2) with redox performance were designed by machine learning. Different metals and their combinations modulated the lattice oxygen properties of titanium dioxide catalysts, thus achieving precise regulation of catalytic performance and product distribution. The results showed that Mn
7V
5TiO
2 had medium ethylene selectivity (55.5%) and high conversion rate (61.8%). The redox capacity was enhanced and both V
5+ and the lattice oxygen species available to oxidative dehydrogenation reaction were enriched by incorporation of atomically dispersed Ce species. Mn
4Ce
2V
7TiO
2 was found to be highly selective for ethylene, with the selectivity of 94.4%. After optimizing the process conditions, Mn
4Ce
2V
7TiO
2 obtained higher ethane conversion (65.2%) and stable ethylene selectivity (89.6%). These results show that Mn
4Ce
2V
7TiO
2 catalyst has great application potential in the oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane.