2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(544i) Effect of Surface Stress on Adhesion of Rough Elastomers
Authors
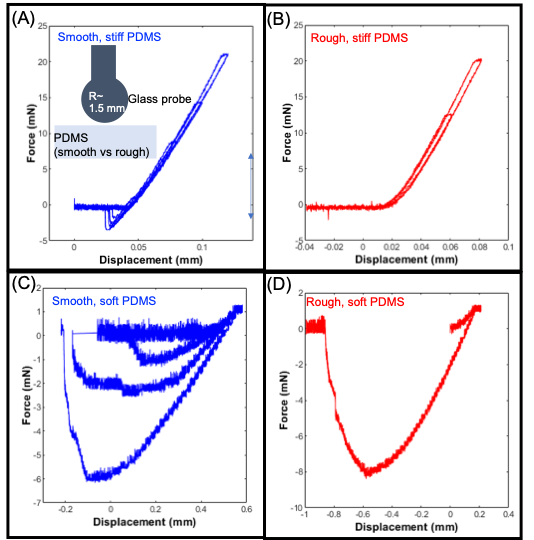
In this study we systematically investigate the effect of surface stress on adhesion of a rough soft solid. We perform adhesion testing with a JKR setup on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) samples of different elastic moduli with a spherical glass probe. We chose two configurations: smooth glass probe on smooth PDMS, smooth glass probe on rough. Roughness of surfaces is characterized using power spectral density (PSD) curves obtained through interferometric height profiling[5, 6]. As shown in the attached figure, adhesion is characterized using the force curve obtained from the JKR setup along with which contact and debonding is also visualized through microscopic imaging.
From our preliminary experiments we observe almost no adhesion for a rough, stiff PDMS. However, for our lowest moduli PDMS, the adhesion increases significantly. This result is in contradiction of the well-known Persson’s theory. We investigate two physical effects to explain our results. Crack trapping in the rougher sample lead to smaller crack length and higher adhesion for rough elastic solids. At the same time, energy to flatten the rough material modulates the surface roughness of the free gel surface and thus affects the adhesion. We will present experimental data investigating the role of surface stress in adhesion of rough and soft material systematically.
Uploaded Figure caption:
(A) Indentation and retraction Force-displacement curve for smooth 10:1 PDMS. Inset: Schematic diagram of JKR setup for adhesion testing with PDMS (2 mm) sample on coverslip probed by a spherical glass rod of fixed diameter. (B) Indentation and retraction Force-displacement curve for rough 10:1 PDMS, showing no adhesion. (C) Indentation and retraction Force-displacement curve for soft, smooth gelest PDMS. (D) Indentation and retraction Force-displacement curve for soft, rough gelest PDMS.
References:
- Fuller, K. and D. Tabor, The effect of surface roughness on the adhesion of elastic solids. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1975. 345(1642): p. 327-342.
- Persson, B. and E. Tosatti, The effect of surface roughness on the adhesion of elastic solids. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2001. 115(12): p. 5597-5610.
- Guduru, P., Detachment of a rigid solid from an elastic wavy surface: theory. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2007. 55(3): p. 445-472.
- Style, R.W., et al., Elastocapillarity: Surface tension and the mechanics of soft solids. Annual Review of Condensed Matter Physics, 2017. 8(1): p. 99-118.
- Hui, C.Y., et al., How surface stress transforms surface profiles and adhesion of rough elastic bodies. Proceedings of the Royal Society A, 2020. 476(2243): p. 20200477.
- Jacobs, T.D., T. Junge, and L. Pastewka, Quantitative characterization of surface topography using spectral analysis. Surface Topography: Metrology and Properties, 2017. 5(1): p. 013001.