Hinokitiol, the ACS molecule of the week in September, 2017 (
https://www.acs.org/molecule-of-the-week/archive/h/hinokitiol.html); was first isolated from the wood of
Chamaecyparis taiwanensis by Japanese scientist Nozone in 1936.
1 Hinokitiol is also a component of the essential oil of the hiba tree (
Thujopsis dolobrata).
2 We have studied hinokitiol because Burke and co-workers
3 have identified hinokitiol as the small biomolecule which maintains cell iron homeostasis and reported the same through their experimental study. Moreover, hinokitiol is, also, of interest as it contains a seven membered aromatic ring in its molecular structure. Yield of hinokitiol is 200 mg per g of hiba tree sawdust and it is reported that conventional sawdust extraction is not adequate to meet the requirements because of this.
2 Hence, the fundamental molecular simulation approach is a cost-effective tool to study the thermodynamic properties of pure hinokitiol. Here, the all-atom optimized potentials for liquid simulations (OPLS-AA) force field with parameters obtained from LigParGen
4 website developed by the Jorgensen group has been adopted in conjunction with the Gibbs ensemble Monte Carlo simulations to predict the vapour – liquid coexistence properties including the critical point and acentric factor which are required as input for classical simulation tools such as equation-of-state methods in process simulation software. The simulations have been performed over a wide temperature range from 530.15 K to 720.15 K, to determine the Clapeyron plot, normal boiling point (T
b), latent heats of vapourization (Δ
vapH), solubility parameters, coexistence densities, critical point and acentric factor (w). The value of Δ
vapH = 46.4 kJ/mol has been determined at the T
b = 530 K. The critical point and w are computed as T
C = 774 K, ρ
C = 0.298 g/cm
3, P
C = 2805.27 kPa and ω = 0.546. These simulation results are in satisfactory agreement with the Marrero-Gani (step wise regression) group contribution method estimates (T
b = 530.014 K, T
C = 762.503 K, ρ
C = 0.345 g/cm
3, P
C = 3365.8 kPa and ω = 0.6544)
5 and will be useful in the design of energy efficient industrial separation processes. Comparison has also been provided with the predictions from Peng-Robinson equation of state.
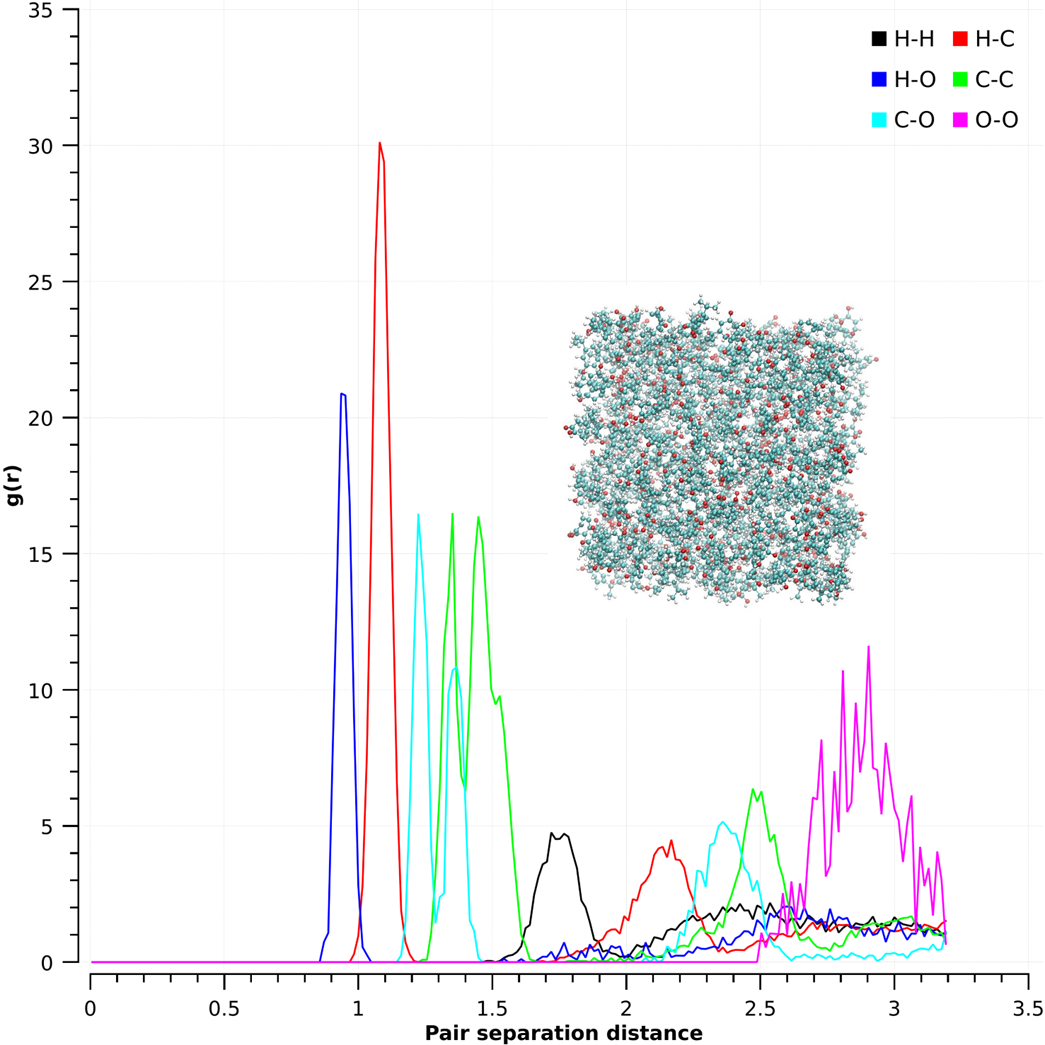
5 Knowledge of the solubility parameter as a function of temperature will allow us to determine the appropriate solvent for liquid-liquid extraction of hinokitiol. Towards the goal of understanding the underlying molecular structure, the O---H intermolecular radial distribution function is employed to estimate the extent of hydrogen bonding present in liquid hinokitiol at 353.15 K and 101.325 kPa. Figure 1 shows all the partial RDFs in the system.
References
[1] Asao T., Ito S. & Murata I. Tetsuo Nozoe (1902−1996). European J. Org. Chem., 899–928 (2004)
[2] Syahmina, A. & Usuki, T. Ionic Liquid-Assisted Extraction of Essential Oils from Thujopsis dolobrata (Hiba). ACS Omega 5, 29618–29622 (2020)
[3] Grillo, A. S.; Santa Maria, Anna M.; Kafina, Martin D.; Cioffi, Alexander G.; Huston, Nicholas C.; Han, Murui; Seo, Young Ah; Yien, Yvette Y.; Nardone, Christopher; Menon, Archita V.; Fan, James; Svoboda, Dillon C.; Anderson, Jacob B.; Hong, John D.; Nicolau, Bruno G.; Subedi, Kiran; Gewirth, Andrew A. ; Wessling-Resnick, Marianne; Kim, Jonghan; Paw, Barry H. & Burke, Martin D. Restored iron transport by a small molecule promotes absorption and hemoglobinization in animals. Science 356, 608–616 (2017).
[4] Dodda, L. S., Cabeza de Vaca, I., Tirado-Rives, J. & Jorgensen, W. L. LigParGen web server: an automatic OPLS-AA parameter generator for organic ligands. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, W331–W336 (2017).
[5] Mohammed Arshak Junais, (2021) Molecular simulation study of solvent extraction of natural products [M. Tech. Thesis, Indian Institute Of Technology Bombay].