2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(410a) Polymeric Mixed Conductors Based on Carboxylic Acid Derivatives for High Performance Organic Electrochemical Transistors
Authors
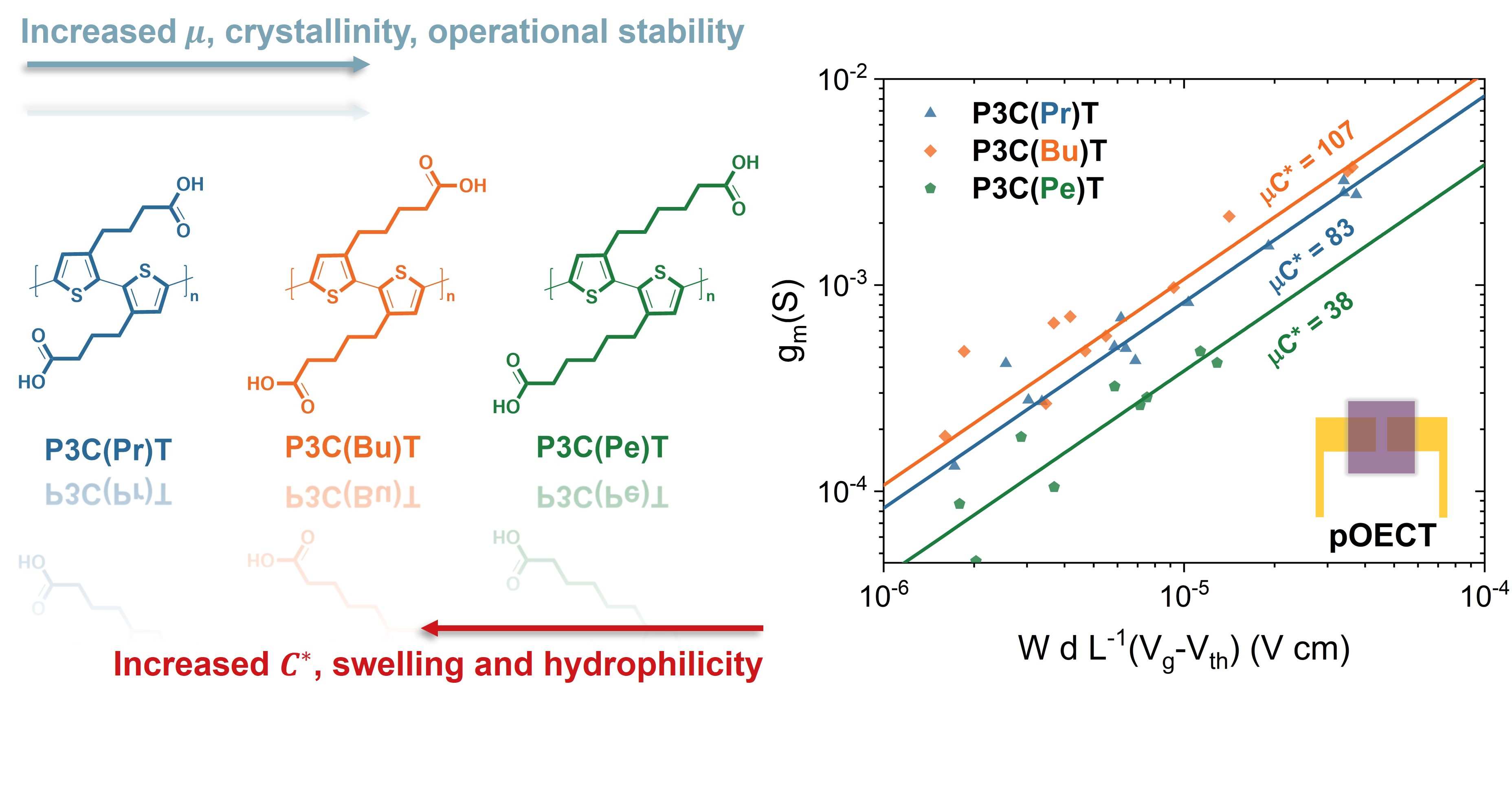
By further benchmarking the materials through planar and interdigitated organic electrochemical transistors (OECTs) and comparing with state-of-the-art OMIECs, we highlight the significant potential of the carboxyl-butyl polythiophene (P3C(Bu)T), which exhibits superior electrochemical performance and faster doping kinetics, achieving a record-high OECT performance among conjugated polyelectrolytes ( = 107 4 ). By further comparing the -COOH moiety with ester functionalization using electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (EQCM-D), we unveiled a distinctive ion transport mechanism, where both cations and anions are involved in the polymer redox process, while pH modulation affects swelling and ion uptake significantly. These findings advance our comprehension of structure-property relationships in conjugated polyelectrolytes, expanding the material landscape for future OMIEC design and development. Further, our work underscores the potential of conjugated polymers featuring alkyl-COOH side chains as a promising avenue for robust OMIEC designs, with the potential to enable facile (bio)chemical functionalization for diverse (bio)sensing applications.