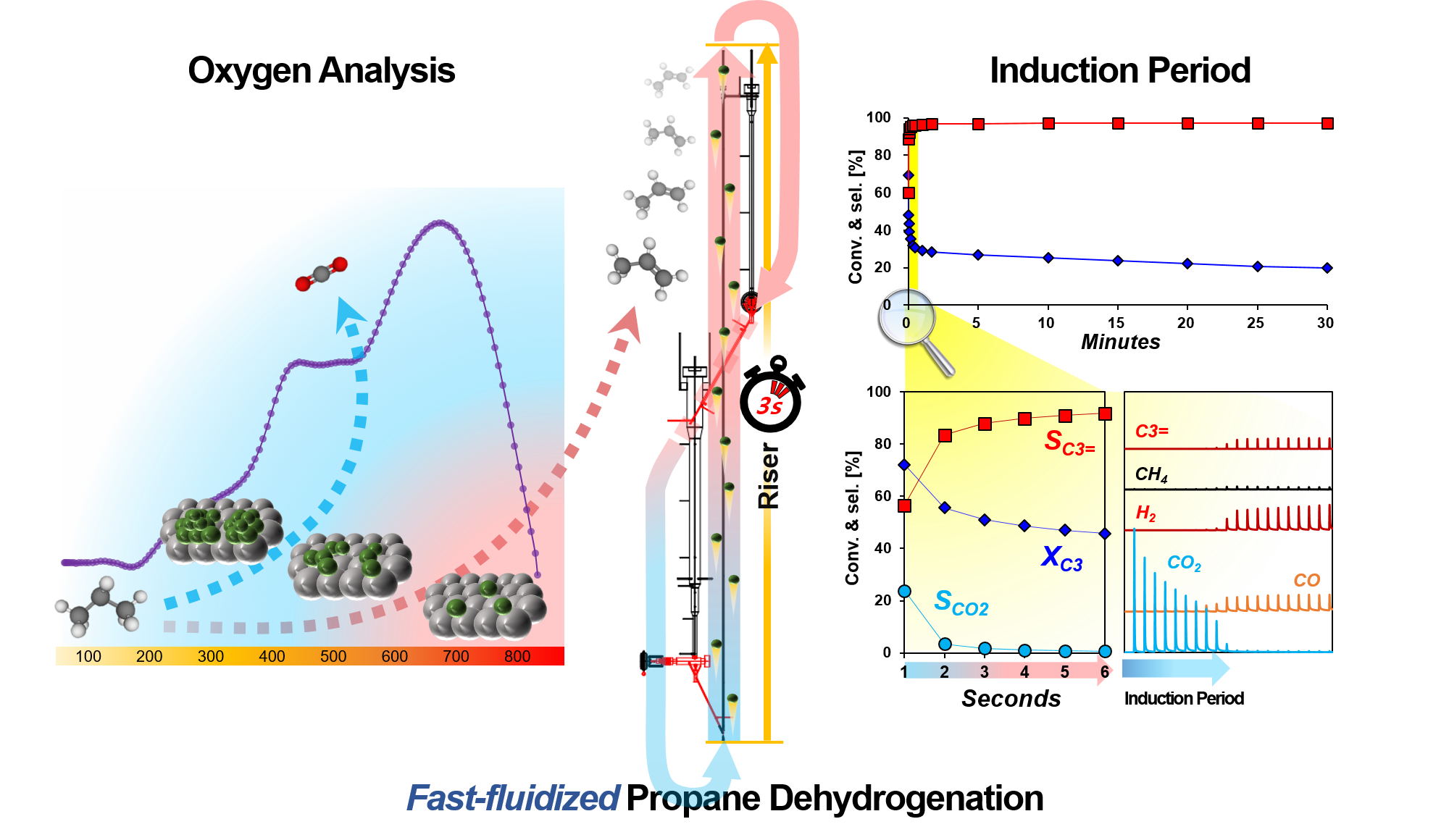
Although a fluidized bed dehydrogenation process with a short residence time is desirable for saving energy, it is challenging to develop a catalyst with high activity and propylene selectivity. Chromium oxide has been identified as a suitable catalyst for propane dehydrogenation (PDH). However, it exhibits an induction period during which COx is formed before the formation of propylene within the very short time-on-stream (a few seconds). In this study, we developed a reaction system for monitoring products on the second timescale and investigated the processes involved in the induction period of PDH, and distinguished the different types of oxygen species derived from chromium oxide. We could establish the correlation between the initial selectivity to propylene and the type of chromium oxide species in the chromium catalyst supported on alumina by O
2-TPO, pulse-reaction, and Raman analyses. Non-selective oxygen species that cause deep oxidation of propane to COx during PDH were generated when the density of chromium on the support was high. The study indicated that most of the propane gas was converted to CO
2 or CO because of the accumulated lattice oxygen over the monolayer on the dispersed chromium species in the catalyst, while chromate species that were well dispersed on the alumina support contributed to high selectivity to propylene in a few seconds of the reaction. We also demonstrate that appropriate reduction of the catalytic CrO
x species can decrease the amount of non-selective oxygen species and that the calcination of the catalyst in an inert atmosphere can enhance product selectivity. In addition, based on this study, propane dehydrogenation was implemented in a bench-scale riser-type fluidized bed reactor using a chromium catalyst.