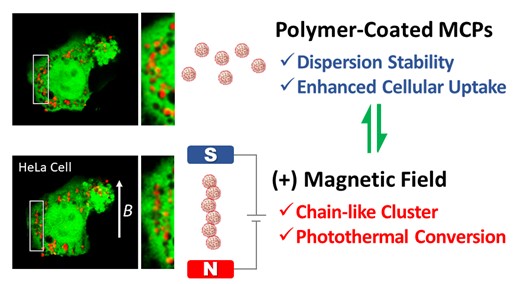
Many photothermal materials have been developed in recent years to achieve efficient photothermal therapy. Although larger-sized materials are preferred to ensure a better photothermal performance, upsizing hampers the cellular uptake of these materials. To overcome this dilemma, we proposed an active control system to manipulate the assembly of magnetic composite particles (MCPs) at the cellular level. Herein, the surface of MCPs were modified with polymer [1] and lipid [2]. These MCPs were then cultured with HeLa cells, and their uptake and localization were investigated.
Using a direct current magnetic field (DCMF (B = 150 mT), the MCPs (diameter: 300 nm) were observed to quickly assemble in cells; however, redispersal did not occur after the DCMF was turned off. To improve the particle dispersibility, polyethyleneimine (PEI) were used to modify the medium-sized MCPs. Coating the MCPs with PEI (a polymer molecular weight of 25,000 or 270,000) improved their dispersibility in phosphate-buffered saline and cellular uptake. In addition, the redispersal of assembled PEI-coated MCPs was observed after the DCMF was turned off (Figure 1). The photothermal conversion efficiency of the MCPs was also improved using the DCMF. To reduce the toxicity of cationic MCPs, pH-responsive cationic lipids were modified on MCPs. Notably, the lipid-coated MCPs exhibited no toxicity by themselves, while they exhibited a cytotoxicity by applying NIR laser and DCMF.
References:
[1] R. Kameda et al., ACS Applied Nano Materials, 6, 3873–3883, (2023)
[2] T. Suzuki et al., AIChE Annual Meeting 2023, presentation no. 620h