2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(244f) Designing Bimetallic Nanoparticles That Catalyze Methyl Cyclohexane Dehydrogenation Using Machine Learning
Authors
Chak Sing Bryan Lee, Nanyang Technological University
Asmee Prabhu, Nanyang Technological University
Tej Choksi, Nanyang Technological University
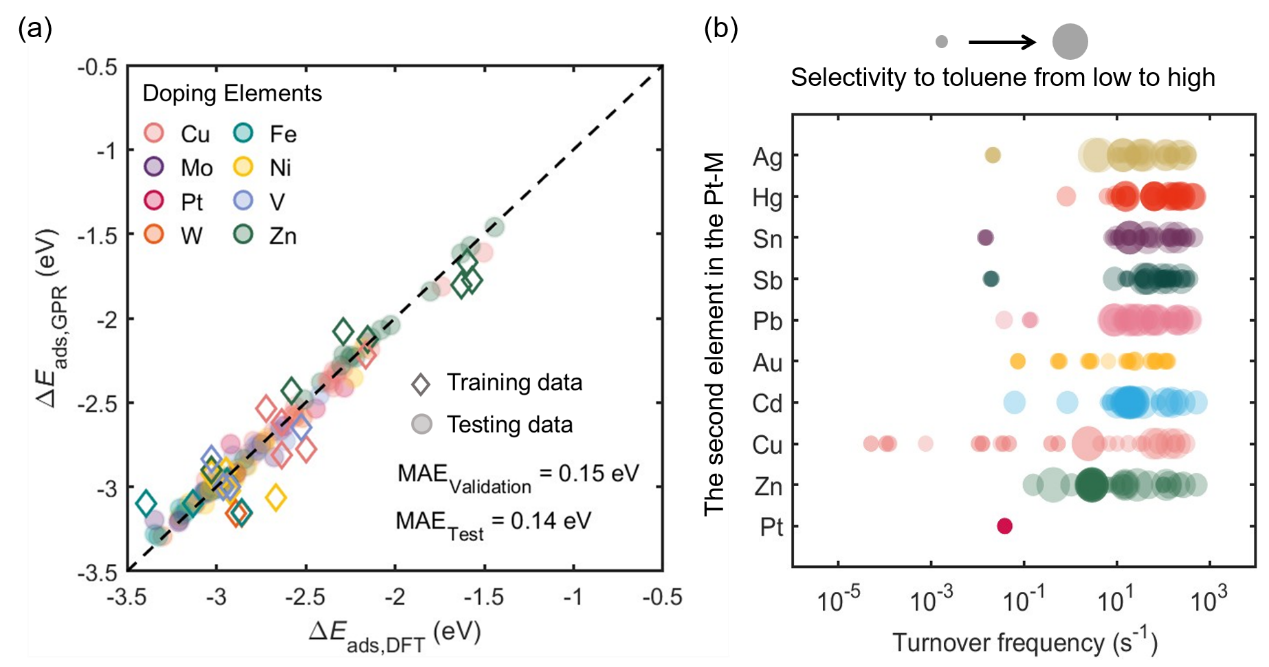
As a promising liquid organic hydrogen carrier, the catalyst design of the dehydrogenation reaction of methyl cyclohexane (MCH) is important for hydrogen storage and transport. Although Pt-based bimetallic nanoclusters (diameter < 2 nm) are used as industrial catalysts of MCH dehydrogenation [1,2], the structure-property relationship for MCH dehydrogenation catalysts needs a systematic understanding to design selective catalysts. To model reaction kinetics in a huge catalyst space, machine learning (ML) assisted first-principle computation has emerged as a powerful tool, demonstrated for heterogeneous catalytic reactions involving small molecules [3]. However, it is challenging to establish a ML model for large cyclic hydrocarbons adsorbed on small nanoclusters, due to the complex multidentate adsorption and the cost of data labelling for constructing training sets. Here, utilising physics-based features, we introduce a cost-effective and accurate ML approach using the Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) algorithm, where active learning reduces the cost of data collection. Trained on a dataset of <100 points, our GPR model achieves a 0.15 eV mean absolute error (Figure a), with excellent transferability to new elements, non-Pt bimetallic sites, and toluene-like unsaturated C7 hydrocarbons. Combining the GPR model with a lumped microkinetic model, we simulated the turnover frequency and selectivity over diverse bimetallic active sites (Figure b). Pt-based nanoclusters with metals possessing a filled d-band like Cu emerge as effective catalysts for MCH dehydrogenation. This machine learning-accelerated screening method, extending to hydrogenation and dehydrogenation of other liquid organic hydrogen carriers, offering a versatile tool for catalyst screening over numerous bimetallic nanoparticles.
[1] Okada Y., Extended abstracts of the 9th Tokyo Conference on Advanced Catalytic Science and Technology, Fukuoka, KL14, (2022).
[2] Meng, J., Zhou, F., Ma, H. et al., Top. Catal., 2021, 64, 509
[3] Mou, T., Pillai, H.S., Wang, S. et al., Nat. Catal.,2023, 6, 122