2024 AIChE Annual Meeting
(231e) Breakthrough Extraction of Aqueous Perfluorooctanoic Acid Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for Sustainable Water Remediation
Authors
Tarek Lemaoui - Presenter, Khalifa University
Ahmad Darwish, Khalifa University
Maguy Abi Jaoude, Khalifa University
Fawzi Banat, The Petroleum Institute
Shadi Hasan, Khalifa University of Science and Technology
Enas Nashef, Khalifa University
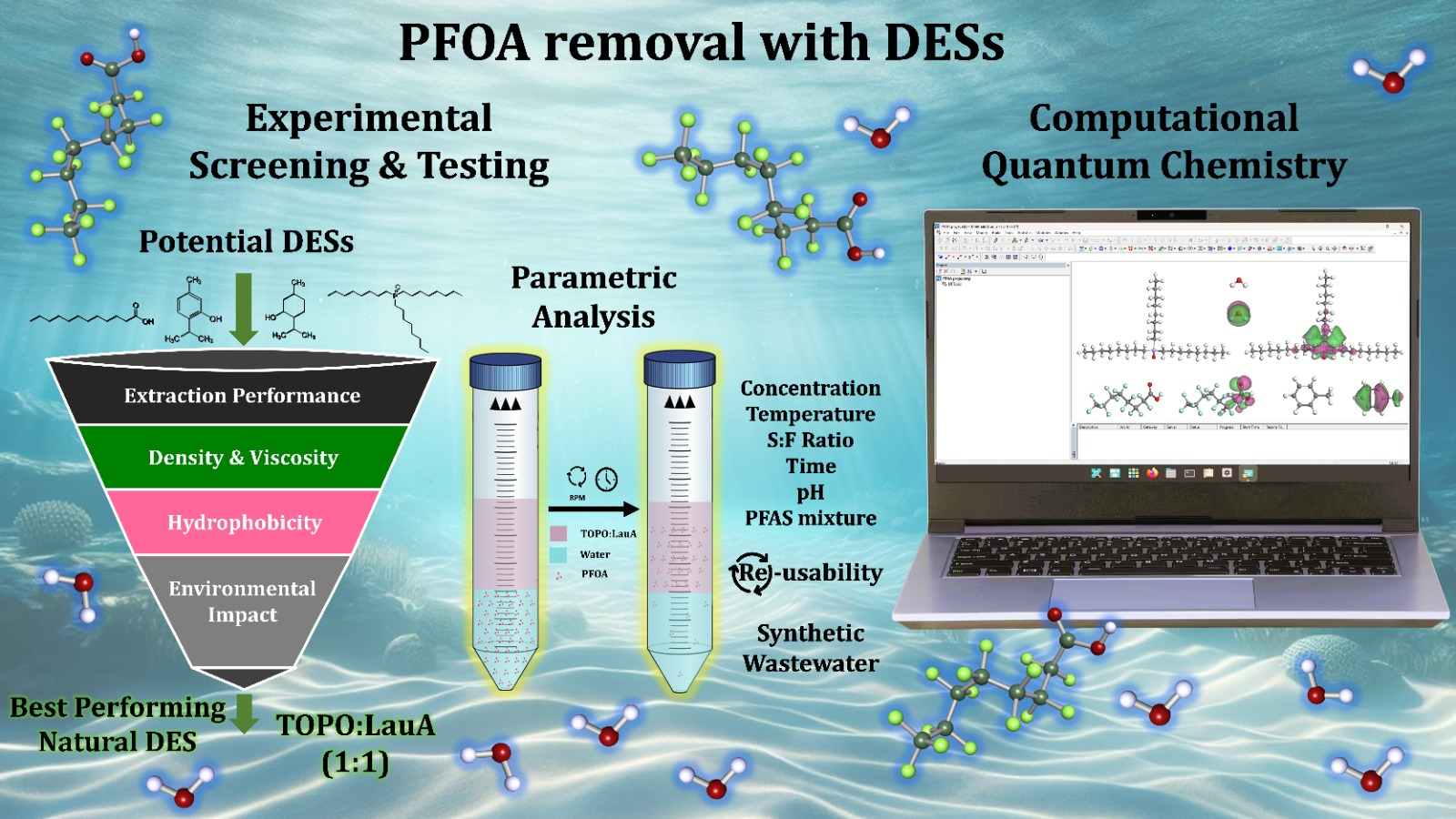
Addressing the urgent need for environmentally sustainable solutions in water remediation, particularly in tackling persistent emerging contaminants such as perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), this work reports for the first-time deep eutectic solvents (DESs) for the extraction of PFOA from aqueous medium. The design framework of the DESs was based on multiple metrics, including extraction performance, density, viscosity, environmental impact, and hydrophobicity. Through the multi-criteria evaluation of ten DESs, trioctylphosphine oxide and lauric acid (TOPO:LauA 1:1) emerged as the superior choice with an exceptional 99.7% extraction efficiency in a single stage only –far outperforming the toluene benchmark’s 82.3%– and showing favorable characteristics across all other assessed criteria. Remarkably, this exceptional efficiency of TOPO:LauA was sustained >98% across diverse operational conditions, including a broad pH and temperature spectrum (3–9 pH; 15–100°C), solvent-to-feed ratios down to 1:7, concentrations as low as 0.1 ppm, rapid equilibration within 1 minute, and reusability throughout seven cycles without any observable degradation, as verified by spectroscopic analysis. TOPO:LauA also demonstrated exceptional selectivity for PFOA even when mixed with other per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and under a complex synthetic wastewater environment. Moreover, computational quantum chemistry modeling was applied, providing insights into the extraction’s molecular mechanism, and showing a strong agreement with the experimental findings. The development of this new DES for the extraction of PFAS signifies a critical breakthrough in water treatment, presenting an alternative that surpasses traditional solvents and conventional methods of PFAS removal, such as adsorption and membranes, in terms of efficacy, sustainability, and scalability.