The solubility and the transport of gases at high pressure and supercritical fluids in polymers is relevant for a variety of different applications, including technological processes such as polymerization or foaming, separation processes by membranes or extraction, and new challenges related to the transport of gases (CO2, natural gas or hydrogen) with the interactions between compressed gases and polymeric components in pipelines, O-rings or liners.
To this aim, a comprehensive model is employed to describe the solubility and permeability of a swelling agent, CO2, and two non-swelling agents, N2 and Ar, in wide range of pressures up to 18 MPa, from sub- to supercritical conditions, and at different temperatures in various polymeric systems: blends of two glassy polyimides (Matrimid and P84), co-polymer Nafion, and two rubbery polymers, namely natural rubber and PDMS.
The experimental trends show complex behaviors, as a consequence of transition from gas-like to liquid-like density of CO2, as well as by that induced by the swelling penetrant to the polymer (glass to rubber).
The Non Equilibrium Thermodynamics (NET-GP) approach for the solubility, and the Sanchez Lacombe lattice fluid theory are used for the representation of solubility properties, while the complementary tool of the Standard Transport Model (STM) provides the description of diffusion, and thus the calculation of the permeability at different temperature and pressures using a self-consistent and physically sound set of parameters.
The model describes well all the solubility and permeability behaviors experimentally encountered, offering a deep insight in the penetrant-induced swelling of the polymer, on its different states. The results obtained from the model investigation and the comparison of swelling and now swelling agents provide also an interesting analysis on the interplay between swelling and mechanical compression at high pressure conditions.
This work takes a step forward in the understanding and predicting the complex interactions between high pressure gases, supercritical CO2 and industrially relevant polymeric materials.
[1] Doghieri, Sarti, Macromolecules 24,7885-7896, 1996.
[2] Minelli, Sarti, J. Membr. Sci. 435, 176–185, 2013.
[3] Houben et al. J. Membr. Sci. 647, 120292, 2022
[4] Shamu et al. J. Supercrit. Fluids 144, 63-70, 2019.
[5] Houben et al. J. Membr. Sci. 620, 118922, 2021
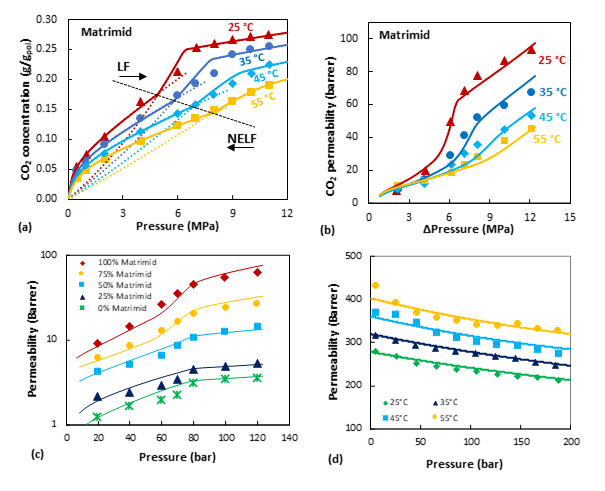
(a) CO2 solubility and (b) permeability in Matrimid at different temperatures, exp. data from [5]; (c) CO2 permeability in Matrimid/P84 blends, exp. data from [3]; (d) N2 permeability in PDMS, Exp. data from [4]; Symbols: experimental data, lines: model calculations