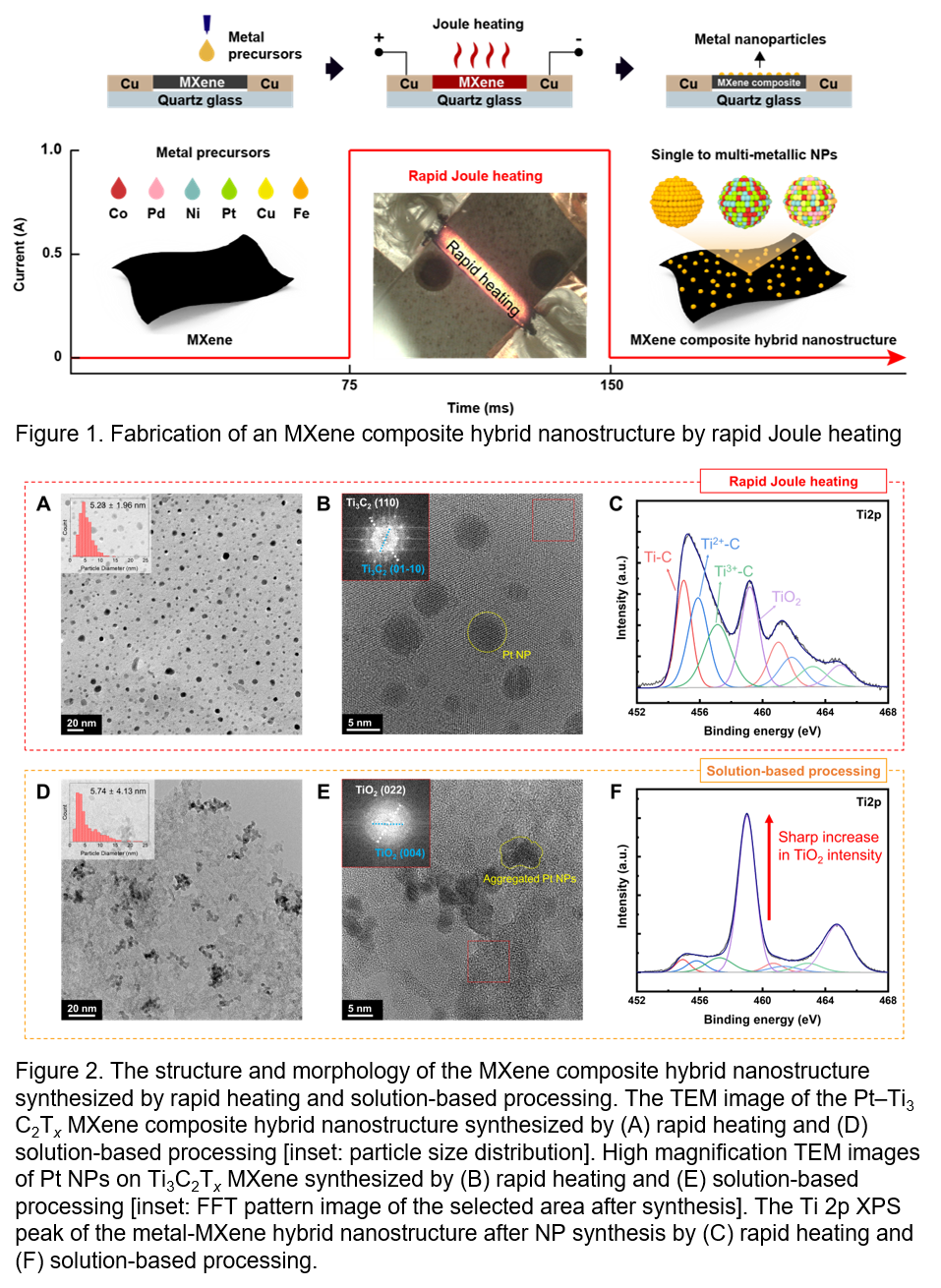
MXene-based nanocomposites have received significant attention due to their potential to enhance electrochemical, electronic, and optical performance by manipulating active sites and surface properties. However, conventional solution-based methods for MXene nanocomposite synthesis lead to severe oxidation of the MXenes, damaging their electrochemical properties. In this study, we demonstrate a solution-free method for synthesizing MXene nanocomposites using rapid Joule heating technique. By loading precursors onto the MXene substrate and subjecting it to a rapid thermal shock, we were able to synthesize hybrids of MXene with various components, including Pt, Co, Cu, Ni, Fe, Pd, and their alloys (Figure 1). Our experimental results show that the rapid Joule heating technique has several advantages over conventional solution-based synthesis methods, including minimized oxidation of the MXenes, uniform distribution of hybrid components, and homogeneous poly-elemental alloy synthesis (Figure 2).
Pt-MXene nanocomposite using the rapid Joule heating technique demonstrated excellent electrocatalytic activity and stability, surpassing the performance of conventional solution-based synthesis. Specifically, the Pt-MXene nanocomposite achieved a hydrogen evolution reduction (HER) overpotential of 43.6 mV and high stability for up to 15 hours, which is over 7.5 times longer than the conventional solution-based synthesis. These improvements over conventional methods are due to preserved active sites on MXenes, uniform distribution of Pt nanoparticles (NPs), and stronger interaction between metal NPs and the MXene substrate resulting from high-temperature of synthesis.
The proposed rapid Joule heating technique enables the successful synthesis of a wide range of hybrid materials without significant loss of MXene properties, making it suitable for various applications where the synergistic effect of MXene composites can yield significant performance enhancements. Overall, our findings provide new insights into the synthesis of MXene-based nanocomposites and open the door to further investigations of their potential in various applications.