2023 AIChE Annual Meeting
(675a) Rate Analysis Implications of (Side) Product Inhibition in Mars-Van Krevelen Redox Cycles
Authors
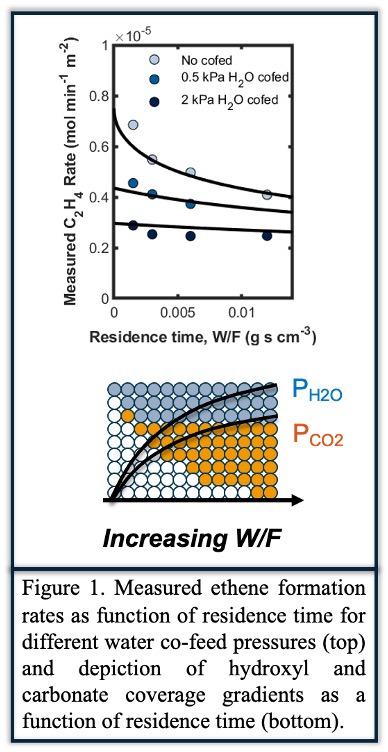
Product co-feed experiments generating differential beds when used to develop Mars-van Krevelen kinetic models for ethane partial and total oxidation are insufficient to explain integral data at low residence times that probe lower ranges of hydroxyl/carbonate coverages than those prevalent in differential co-feed experiments. Measured (average) rates deviate from true ones even at conversions as low as 0.1%, with apparent rates being more sensitive to residence time at low, rather than high conversions (Figure 1). Estimation of rate parameters and mechanisms over excess oxygen-containing nickel oxide requires consideration of inhibitory effects of both water and CO2, unlike those over niobium-containing nickel oxides that carry exclusively lattice oxygens recalcitrant to carbonate formation. In this talk, we will describe how the quasi-equilibrated nature of recombinative water desorption steps in Mars-van Krevelen cycles result in an amplification of rate inhibitory features that are critical to consider during kinetic analysis of alkane oxidation over bulk oxides more generally.