2023 AIChE Annual Meeting
(521ac) Molecular Catalyst-Functionalized Silicon Photocathode for Aqueous Photoelectrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to Methanol
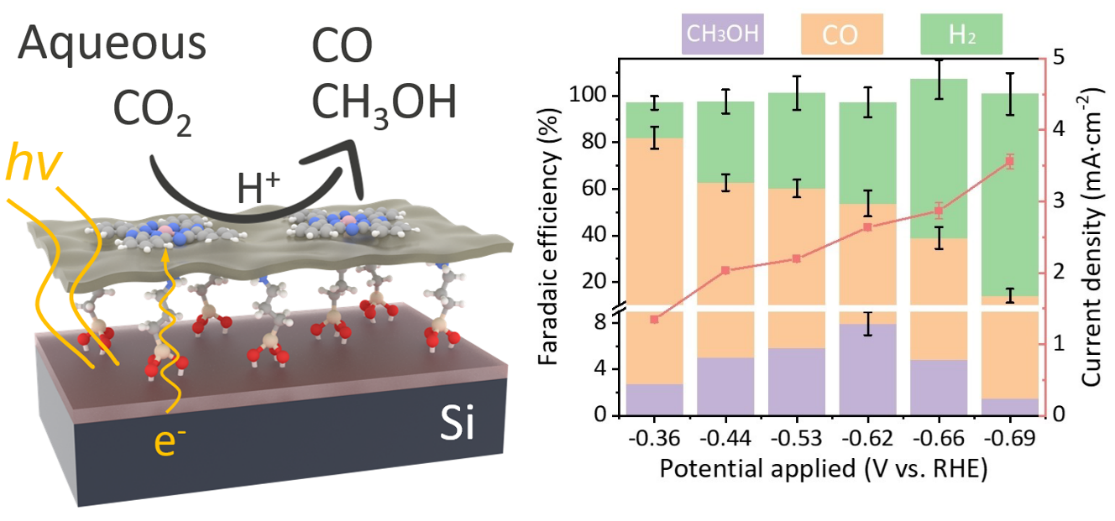
This work puts forth a strategy for interfacing molecular catalysts to p-type semiconductors and demonstrates state-of-the-art performance for photoelectrochemical COÂ2 reduction to CO and methanol.
References
(1) Shang, B.; Zhao, F.; Choi, C.; Jia, X.; Pauly, M.; Wu, Y.; Tao, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Harmon, N.; Maggard, P. A.; Lian, T.; Hazari, N.; Wang, H., Monolayer Molecular Functionalization Enabled by AcidâBase Interaction for High-Performance Photochemical CO2 Reduction. ACS Energy Letters 2022, 7 (7), 2265-2272.
(2) Shang, B.; Rooney, C. L.; Gallagher, D. J.; Wang, B. T.; Krayev, A.; Shema, H.; Leitner, O.; Harmon, N. J.; Xiao, L.; Sheehan, C., Aqueous Photoelectrochemical CO2 Reduction to CO and Methanol over a Silicon Photocathode Functionalized with a Cobalt Phthalocyanine Molecular Catalyst. Angewandte Chemie 2023, 135 (4), e202215213.