2023 AIChE Annual Meeting
(367e) Characterization of the Curing Kinetics and Structure of Coal-Based Phenolic Resin Composites
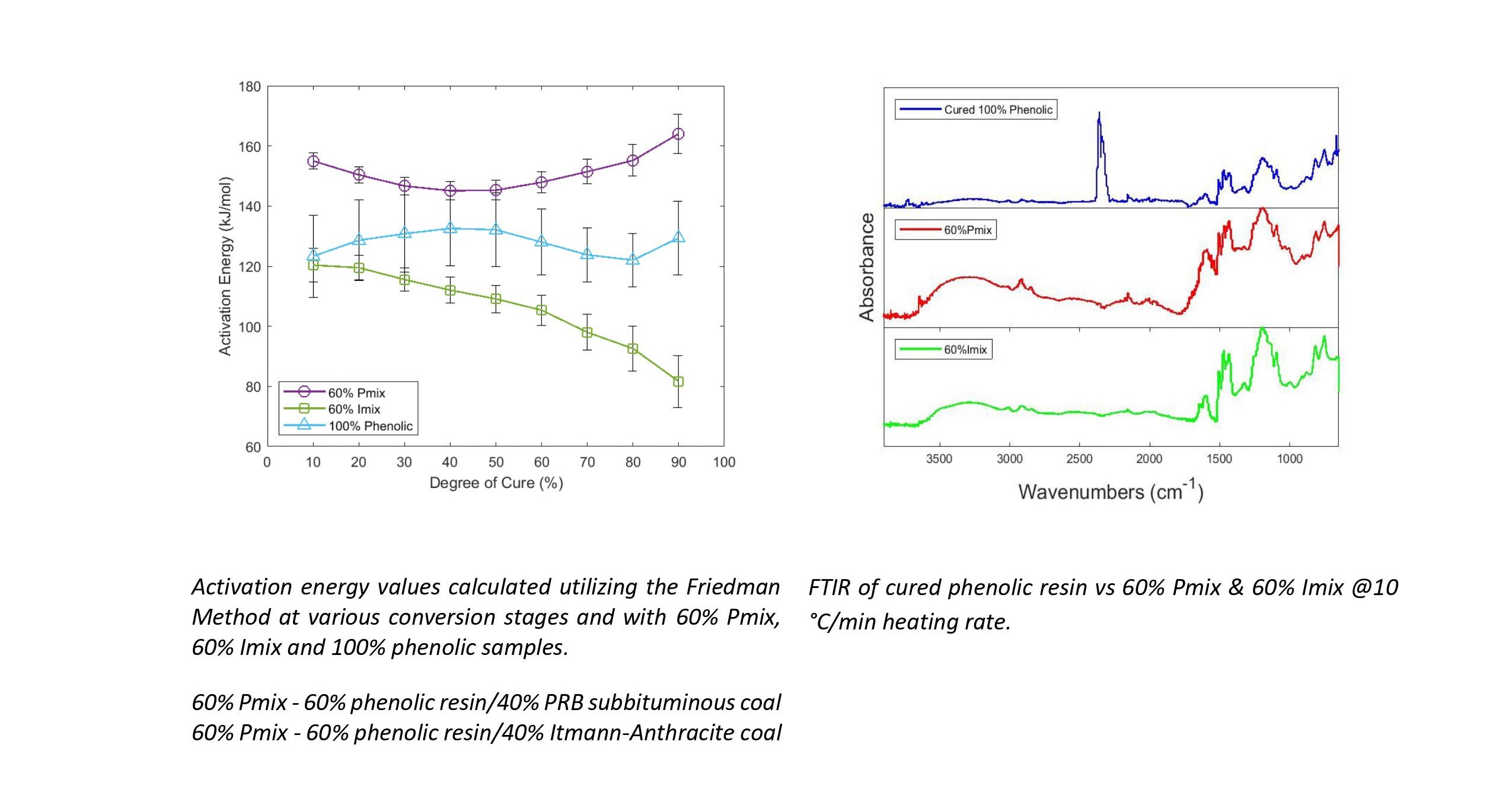
In this work we investigated the effect of coal rank and content on the curing of phenolic resin using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Dynamic measurements were used to evaluate certain thermal properties like the peak temperature, heat of reaction and activation energy. Two ranks of coal were selected due to functionality differences â anthracite and sub-bituminous coal type, and their content were utilized at varied filler weight percentages within the sample mix. Initial results from DSC analysis using a 40% filler weight content of both ranks of coal within the sample mix revealed an increased activation energy effect on the curing of phenolic resin with the sub-bituminous ranked coal (which could be attributed to the presence of a higher number of functional end groups) relative to the anthracite-ranked coal. For further interrogation of these results, the cured samples were characterized using FTIR and solid-state 13C NMR. Preliminary results from the FTIR analyses reveals a disappearance of aromatic isocyanate bonds (N=C=O) in the 40% coal-filled phenolic samples compared to the 100% phenolic, which suggests the possible interaction between the coal particles and the phenolic resin during cure. Results from the CNMR analysis was carried out to further elucidate the structural behavior of these cured samples and would be discussed during the presentation.
This talk would focus on reporting these experimental observations, along with additional results using a varied range of coal-filler weight content and correlating the curing properties to the structural characterization of the coal-based phenolic resin. The effects of the coal-filler on phenolic resin would be highlighted based on its ranks and filler content using the methods outlined in this study.