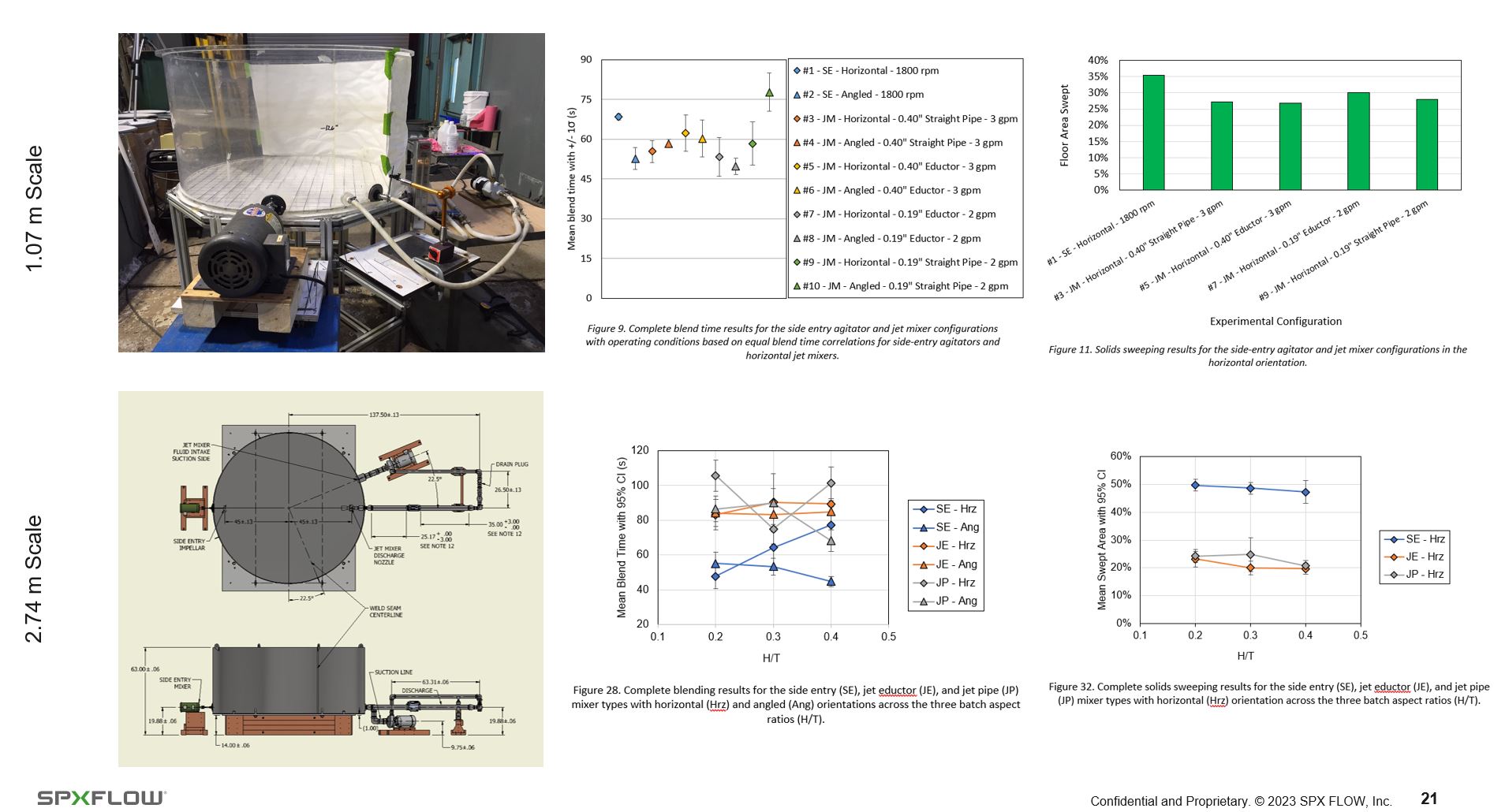
Vessels with low liquid height to tank diameter aspect ratios (H/T) are prevalent in the Energy sector and appear elsewhere across industries. Performing mixing operations in large vessels (i.e., greater than 10 m) with low H/Ts can be challenging and requires specialized equipment. Top-entry agitators are not economically viable. Two viable options include jet mixers and side-entry mixers. As a manufacturer of top-entry agitators, side-entry agitators, and centrifugal pumps, SPX FLOW has a vested interest in understanding the strengths and weaknesses of jet mixing and side-entry mixing and recommending suitable mixing equipment to its clients. An experimental comparison of blending and solids sweeping performance was conducted to further enhance and prove out the understanding of jet mixing and side-entry mixing in vessels with low H/Ts.
The investigation was conducted across two scales (1.07 m and 2.74 m). Three liquid height to tank diameter aspect ratios were investigated between the two scales (0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 H/T). Vertically angled and horizontal mixer orientations were investigated across both scales and types of mixing equipment. The jet nozzle diameter to tank diameter ratios (D/Ts) ranged between 0.005 and 0.013. The impact of jet nozzle geometries, including eductors, were investigated. The side-entry impeller diameter to tank diameter ratios ranged between 0.036 and 0.056 D/T.
Water was used as the bulk fluid. Blending trials in the 1.07 m scale were conducted with 6M NaOH and 6M HCl additions using phenolphthalein as a visual indicator. Blending trials in the 2.74 m scale were conducted with 0.1% volume fraction additions of a saturated NaCl solution and monitored via conductivity measurements. Solids sweeping trials were conducted at both scales using a slow-settling resin representative of sludge in energy or environmental applications and measured with grids marked on the vessel floors. The 1.07 m scale trials were conducted at similar theoretical mixing power as measured mixing powers were on the order of 1 W, were unreliable, and fell within instrumentation errors. The 2.74 m scale trials were conducted at equivalent measured system powers of 0.125 W/kg for blending and 0.109 kW for solids sweeping.
Blending and solids sweeping results were compiled and compared. Mean blend times and mean swept areas were calculated with 95% confidence intervals. Experimental blend time results were compared to theoretical blend time predictions (R. Grenville and J. Tilton, 1991; R. Kehn, 2011).
Conclusions drawn from the 1.07 m scale were:
- Jet mixers and side-entry mixers provided similar blending performance at similar theoretical mixing power.
- Jet mixers and side-entry mixers provided similar solids sweeping performance at similar theoretical mixing power.
- Blending and solids sweeping performance was independent of jet mixer nozzle geometries, including eductors.
- Blending performance was independent of mixer orientation (i.e., horizontal or angled).
- Solids sweeping performance was dependent on mixer orientation.
Conclusions drawn from the 2.74 m scale were:
- At equivalent system power, jet mixer blending performance trailed side-entry mixer.
- At equivalent system power, jet mixer solids sweeping performance trailed side-entry mixer.
- Blending and solids sweeping performance was independent of jet mixer nozzle geometries, including eductors.
- Blending performance was considered independent of mixer orientation except there were indications that angled mixers may perform better as H/T aspect ratios increased.
References:
- Grenville and J. Tilton, "A new approach to correlation of blend time data from turbulent jet mixed vessels," 1991.
- Kehn, "Comparing Top Entry Versus Side Entry Agitator Performance in Low Viscosity Blending," The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, vol. 89, 2011.