2023 AIChE Annual Meeting
(154r) Reactive Compatibilization of Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate/Recycled Rubber Particles Blends
Authors
Erfan Dashtimoghadam, Center for Materials and Manufacturing Sciences, Troy University
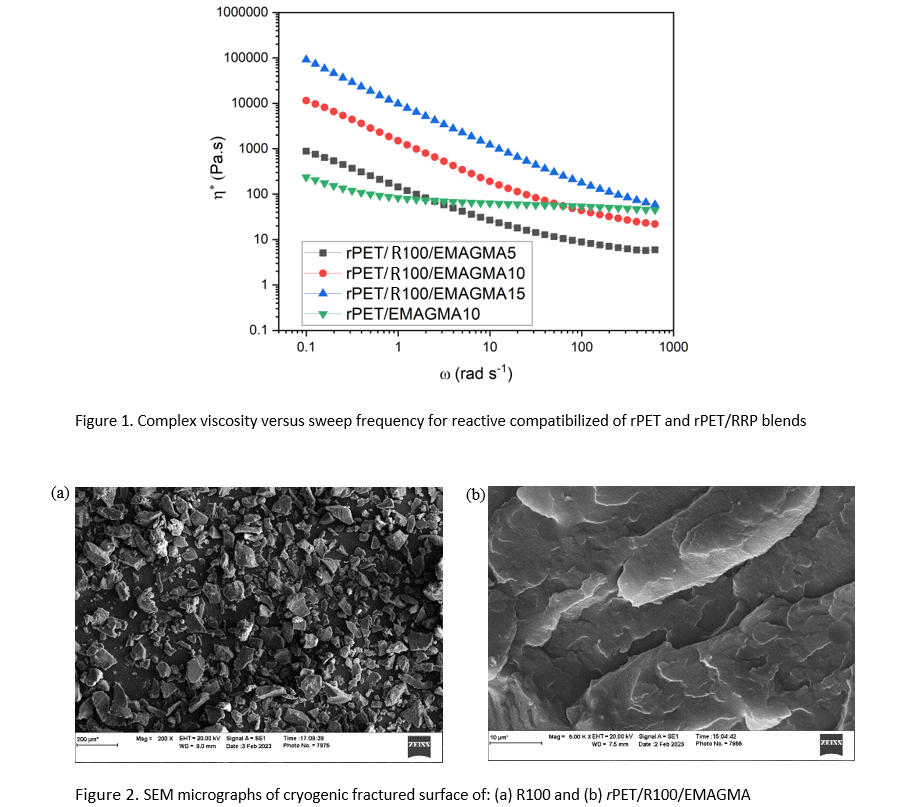
A blend of incompatible polymers such as recycled polyethylene terephthalate (rPET) and recycled rubber particles (RRPs) can have poor mechanical and impact properties because polymeric phases interact weakly and segregate when mixed. This study investigates compatibilization of rPET and RRPs blends. Polystyrene-block-poly(ethylene-ran-butylene)-block-polystyrene-g-maleic anhydride (SEBS-g-MA), poly (ethylene-co-glycidyl methacrylate) (EGMA), and poly (ethylene-co-methyl acrylate-co-glycidyl methacrylate) (EMAGMA) were used as reactive compatibilizers. The rheological properties of the compatibilized blends were characterized and compared with non-compatibilized blends. The results showed that the reactive compatibilizers improved the interfacial adhesion RRPs in rPET matrix, leading to enhanced impact strength. Complex viscosity of rPET/RRPs blends were found to increase with increasing compatibilizer content, indicating enhanced melt strength and processability. Morphological analysis by scanning electron microscopy revealed a uniform dispersion of RRPs in the compatibilized blends, confirming increased interfacial interactions. These findings suggest that the reactive compatibilization is an effective strategy to optimize rPET/RRPs compounds, suitable for continuous manufacturing and melt extrusion.