2023 AIChE Annual Meeting
(152d) Enhanced Extraction of Tea Tree Oil By Hydrodistillation with an Alkyl Polyglucoside Surfactant
Authors
Duu-Jong Lee - Presenter, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology
Bing-Hung Chen - Presenter, National Cheng Kung University
Wan-Chien Ton, National Cheng Kung University
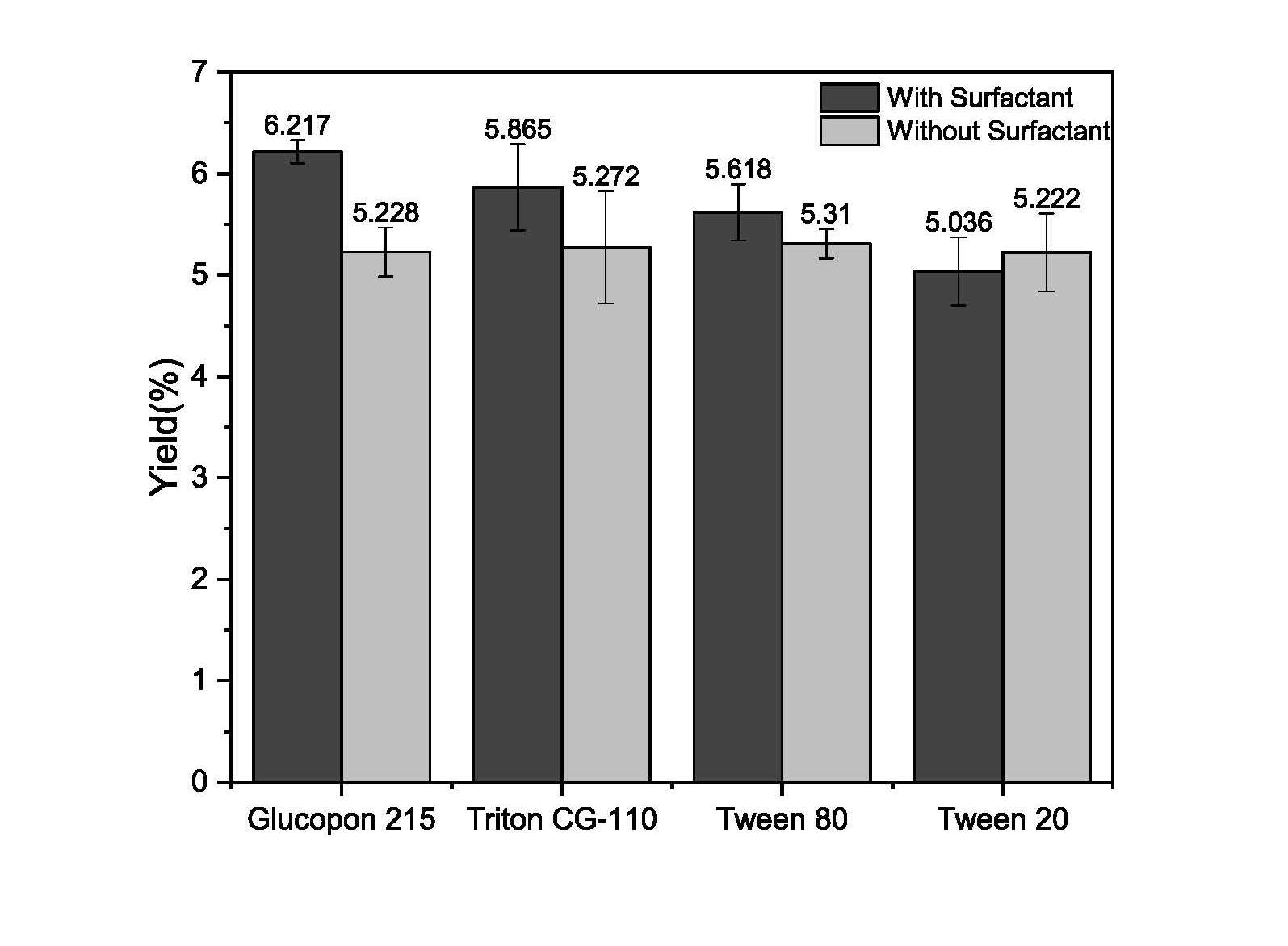
In this study, the surfactant-enhanced extraction of tea tree oil (TTO) was carried out by hydrodistillation in a Clevenger apparatus using the aqueous solution of a nonionic alkyl polyglucoside (APG) surfactant, Glucopon 215 UP. Tea tree oil is the volatile essential oil derived mainly from the Australian native plant Melaleuca alternifolia. Response surface methodology (RSM) with central composite design (CCD) was performed to determine the optimum condition and to optimize the oil yield. The reaction variables being optimizes were surfactant concentration (X1), extraction time (X2) and the mass ratio of liquid extractant to dried tea tree leaves ratio (X3). From the analysis of variance (ANOVA), the most influential parameter on TTO yield was the extraction time. The predicted yield was found in good agreement with the empirical value, while the optimal process parameters were (1) 353 ppm for surfactant concentration, (2) 174 min as extraction time, and (3) with a liquid/solid ratio of 24.6. For comparison, experiments were carried out at optimal condition but without surfactant present in extractant. It was found that the extraction yield increased by 1.18 times in presence of Glucopon 215 UP. Modeling of the distillation process is considered the fundamental step in establishing an efficient and scalable industrial process [1]. The hydrodistillation of tea tree oil was conducted under the optimal condition to examine the established kinetics model. The result showed that extraction process closely fit the model of instantaneous washing followed by diffusion and a higher mass transfer coefficient was founded in the presence of surfactant. The composition of produced TTO and its solubility with Glucopon 215 aqueous solution was performed with GC-FID and HPLC. Terpinen-4-ol was the dominant ingredient and solubility was linearly increased with surfactant concentration. In antioxidant study, α,α-diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging method was applied for evaluating the potential antioxidant component in tea tree oil. The antioxidant activities decreased in the following order: Terpinolene > γ-terpinene > α-terpinene.
Keywords: Melaleuca alternifolia (Tea Tree) Oil; Nonionic surfactant; Extraction; Optimization
[1] Dao, T.P., N.Q. Tran, and T.T. Tran, Assessing the kinetic model on extraction of essential oil and chemical composition from lemon peels (Citrus aurantifolia) by hydro-distillation process. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2022. 51: p. 172-177.