Breadcrumb
- Home
- Publications
- Proceedings
- 2022 Annual Meeting
- Catalysis and Reaction Engineering Division
- Reaction Chemistry and Engineering I
- (8b) Continuous Flow Calorimetry for the Thermal Characterization of Highly Exothermic and Fast Reactions

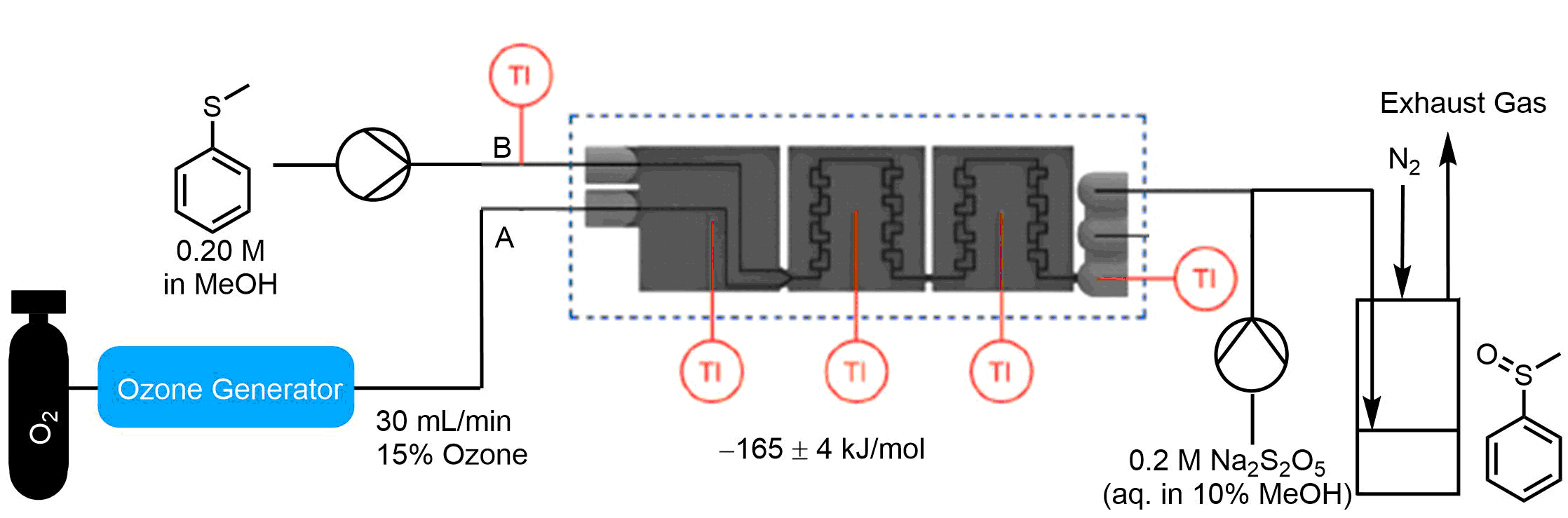
Initially, a benchmarking study for a very exothermic reaction will be presented to compare the performance against existing literature values. Subsequently, a more complex organolithium transformation which resulted in the formation three products will be discussed. The selectivity towards the different products was carefully optimized (flow rate, reagent equivalents, temperature) through a design of experiments (DoE) study. The influence of mixing efficiency on conversion and product selectivity was investigated through computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. The understanding obtained from the DoE study and CFD simulations was then used to identify the best flow conditions to measure the calorimetric data. Finally, the utilization of continuous flow calorimetry to investigate the ÎHrxn for a gas-liquid ozonolysis reaction using ozone (O3) (Fig. 1) operating within an annular flow regime will be highlighted.3
(1) J. Yoshida et al., Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9896-9904.
(2) M. C. Maier et al., React. Chem. Eng. 2020, 5, 1410-1420.
(3) D. Polterauer, et al., React. Chem. Eng. 2021, 6, 2254-2258.