2022 Annual Meeting
(707c) Highly Ordered Copper Nanowire Array As Active Electrocatalysts for CO2 Reduction Reaction
Authors
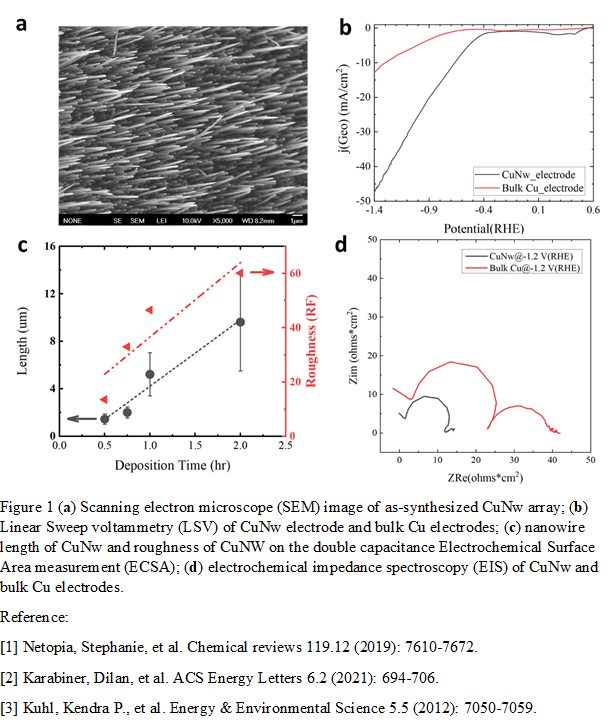
Herein, we report a novel catalyst design, i.e., Cu nanowire (CuNw) electrode with highly ordered vertical alignment, to enhance the catalytic performance of CO2RR-to-C2+. The nanowire was synthesized via the template-assisted electrodeposition method. SEM imaging confirmed the formation of 200-nm diameter nanowire with needle-tip morphology (Figure 1a). We then performed CO2RR over this CuNw using a H-cell reactor. Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV) study indicated a high geometric current density over the CuNw electrode, -47 mA/cm2 at -1.4 VRHE, which is about 4 times higher than that of the bulk Cu (Figure 1b). The electrochemical surface area (ECSA) measurements showed that the roughness of CuNw increased by 20- to 60-fold when compared to the bulk Cu (Figure 1c), suggesting that the high activity might come from the higher surface area of CuNw. In addition, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurement showed that there is less charge transfer resistance on the CuNw electrode than the bulk Cu electrode (Figure 1d). NMR measurements showed that the partial current of CO2RR-to-ethanol over the CuNw was 3-fold higher than that of the bulk Cu. Overall, our study provides a novel, convenient, and scalable catalyst design of ordered Cu nanowire array structure for electrocatalysis.