Methane (CH
4) is a vital energy carrier and chemical feedstock but has more than 80 times the global warming potential of CO
2 over a 20âyear span [1]. Thus, complete catalytic oxidation of CH
4 to CO
2 is often desirable to reduce the environmental impact of CH
4Â emissions by more than 96% while generating far less NO
Âx compared to thermal combustion. Pd/Al
2O
3 catalysts are state-of-the-art for CH
4 oxidation around 500 ºC under CH
4-rich conditions but require high precious metal loadings (> 5%) and cannot maintain sufficient CH
4 conversion (> 90%) at lower temperatures (< 400 ºC) or under lean/ultraâlean conditions [2]. Additionally, H
2O and sulfur poison Pd sites and metal dispersion is lost through sintering upon regeneration at high-temperatures, resulting in decreased CH
4 oxidation performance and shortened catalyst life. Recently, Pd-containing high-silica zeolites, such as Pd/SSZ-13 (CHA topology), have emerged as promising catalysts for lowâtemperature CH
4 oxidation owing to their hydrophobicity and superior hydrothermal durability [3].
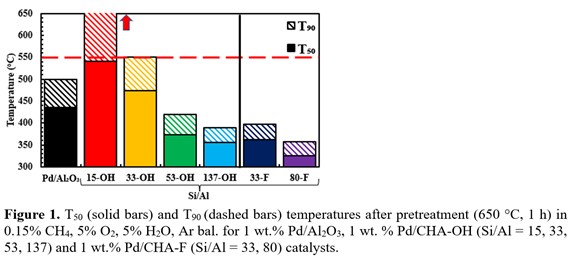
High-silica CHA zeolites (Si/Al molar ratios = 15-137) were prepared in both hydroxide (OH) and fluoride (F) media, ion-exchanged to 1 wt.% Pd, and then evaluated for CH4 oxidation activity before and after simulated aging for 1 h at 650 ºC under wet-lean conditions (0.15% CH4, 5% O2, 5% H2O, bal. Ar). A comparison of temperatures required to achieve 50% and 90% CH4 conversion (T50, T90), revealed that Pd/CHA (Si/Al > 33) outperforms Pd/Al2O3 (Figure 1) with steady-state CH4 oxidation rates on Pd/CHAâF (80) were ~4à higher than Pd/Al2O3 at 250 ºC (0.4 % CH4, 5% O2, N2 bal.). Decreasing T50 and T90 temperatures for Pd/CHA with increasing Si/Al molar ratios and results for Pd/CHAâOH (137) and Pd/CHA-F (80) of similar Si/Al ratio suggest that more hydrophobic zeolites result in improved lower temperature performance and durability in the presence of H2O.
References
- Solomon, S., Manning, M., Marquis, M., Qin, D. Cambridge University Press (2007).
- Raj, A., Matthey Technol. Rev. 2016, 60, 228.
- Dusselier, M.; Davis, M. E., Rev. 2018, 118, 5265.