2020 Virtual AIChE Annual Meeting
(614g) Synthesis of Mo4VAlC4 MAX Phase and Two-Dimensional Mo4VC4 Mxene with Five Atomic Layers of Transition Metals
Authors
Christopher Shuck - Presenter, Drexel University
Grayson Deysher, Drexel University
Nathan Frey, University of Pennsylvania
Alexandre Foucher, University of Pennsylvania
Kanit Hantanasirisakul, Drexel University
Kathleen Maleski, Drexel University
Asia Sarycheva, Drexel University
Vivek Shenoy, University of Pennsylvania
Eric A. Stach, Purdue University
Babak Anasori, Drexel University
Yury Gogotsi, Drexel University
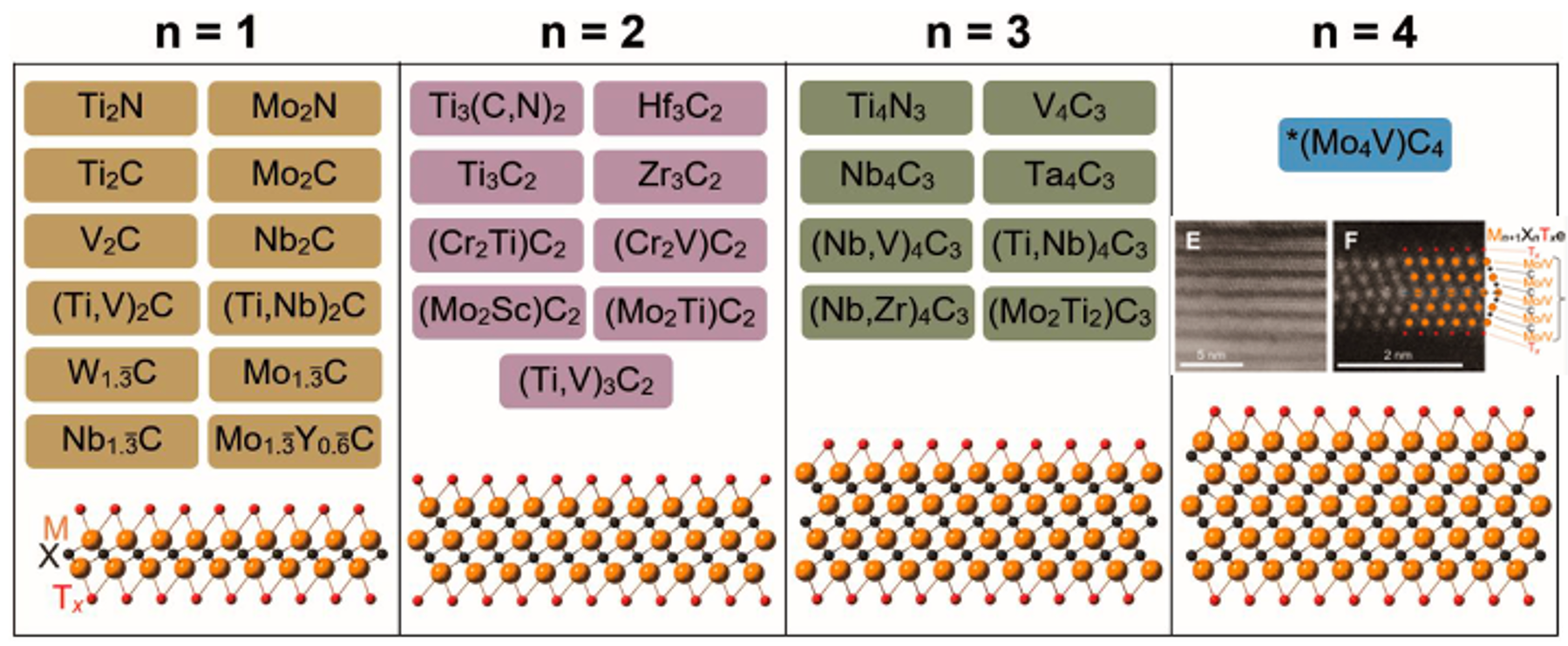
MXenes have a general formula of Mn+1Xn, typically described as n=1-3, where M is a transition metal (Ti, Nb, V, Mo, etc.) and are interleaved with layers of C and/or N (shown as X). Here, we report on the synthesis and characterization of the first MXene Mo4VC4), with 5 atomic layers (n=4), as well as its precursor, Mo4VAlC4. TEM and XRD showed the structure of this phase is P63/mmc similar to other MAX phases. However, this structure has a twinned set of M-layers, unique in the MAX/MXene family. Compositionally studied via EDS and XPS, the MXene composition was determined to be Mo4.10V0.90C2.99. HRSTEM, Raman spectroscopy, and DFT indicate that the crystal structure contains a solid solution of Mo and V. DFT calculations also indicate that other n=4 transition metal MAX phases (M'4M"AlC4) may be possible, suggesting that more M5C4Tx MXenes can potentially be synthesized. In addition, UV-vis-NIR spectroscopy, temperature-dependent resistivity measurements, and thermogravimetric analysis provide additional characterization on the optical, electronic, and thermal properties of this new Mo4VC4 MXene. This study provides a new subfamily of MXenes with five atomic layers of transition metals, allowing for wider range of compositions for more control over properties.