2020 Virtual AIChE Annual Meeting
(586a) Styrene Hydroformylation on Rh-Based Intermetallic Catalysts
Authors
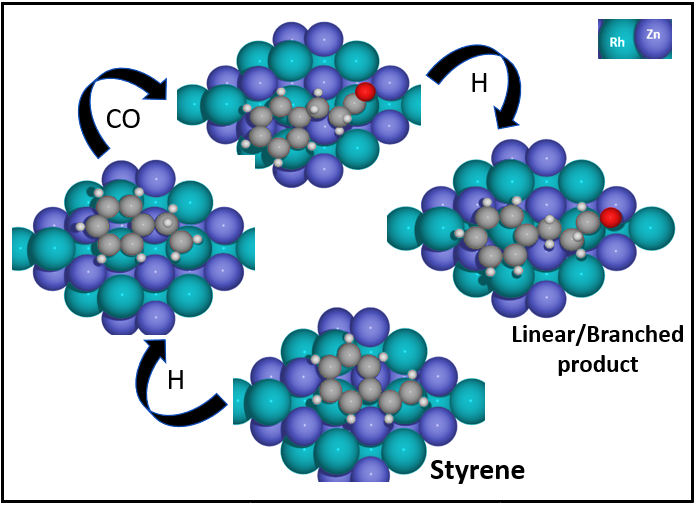
In this presentation, we describe a combined theoretical and experimental approach toward understanding reaction mechanisms of styrene hydroformylation on intermetallic surfaces. We utilize density functional theory (DFT) calculations of hydroformylation thermochemistry and kinetics to elucidate the detailed reactivity of several low-energy RhZn surfaces (ZnRh(100), ZnRh(111), ZnRh(210), ZnRh(110)), toward the overall goal of understanding the nature of the active site for this reaction and the reason for the significantly improved activity relative to pure Rh(111). Our results suggest that alloying Rh with a relatively inactive metal such as Zn weakens the binding of surface intermediates; the reaction landscape is therefore considerably impacted by the relative amounts of Zn and Rh found on the considered surfaces. Theoretical results are considered in the context of experimental studies of styrene hydroformylation on intermetallic RhZn supported on mesoporous SBA-15. These experimental results show our intermetallic RhZn outperforms a benchmark homogeneous catalyst.
References
- Hou, C.; Zhao, G.; Ji, Y.; Niu, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Nano Research 2014, 7 (9), 1364-1369.
- Wang, L. B. et al., Nature Communications 2016,
- Miyazaki, M., Furukawa, S., Komatsu, T. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18231â18239.